What is an Economic Venture?

An economic venture refers to any activity or project undertaken with the goal of generating financial returns or creating economic value. It encompasses a wide range of initiatives, from small-scale startups to large corporate investments, all aimed at producing goods, services, or innovations that meet market demands. Economic ventures are driven by entrepreneurship, risk-taking, and strategic planning, often requiring resources such as capital, labor, and technology. They play a crucial role in economic growth, job creation, and societal development. Understanding the nature of economic ventures is essential for aspiring entrepreneurs, investors, and policymakers seeking to foster sustainable and profitable business ecosystems.
What is an Economic Venture?
An economic venture refers to any activity or project undertaken with the primary goal of generating economic value, such as profit, revenue, or financial growth. It involves the allocation of resources, such as capital, labor, and time, to create goods, services, or solutions that meet market demands. Economic ventures can range from small-scale startups to large multinational corporations, and they play a crucial role in driving economic development and innovation.
See Also What Are the Positions at Vc Firms?
What Are the Positions at Vc Firms?1. Key Characteristics of an Economic Venture
An economic venture is defined by several key characteristics. First, it involves risk-taking, as there is no guarantee of success. Second, it requires investment in resources like money, time, and effort. Third, it aims to create value for customers, stakeholders, and society. Lastly, it operates within a competitive market environment, where innovation and adaptability are essential for survival.
2. Types of Economic Ventures
Economic ventures can be categorized into various types based on their size, scope, and purpose. These include small businesses, startups, social enterprises, and large corporations. Each type has unique goals and challenges. For example, startups often focus on innovation and rapid growth, while social enterprises prioritize social impact alongside financial sustainability.
See Also How Do You Calculate the Pro Rata Entitlement for an Existing Investor in a Company as the Company Raises a New Round of Funding
How Do You Calculate the Pro Rata Entitlement for an Existing Investor in a Company as the Company Raises a New Round of Funding3. Importance of Economic Ventures in the Economy
Economic ventures are vital for economic growth and development. They create jobs, stimulate innovation, and contribute to GDP. By addressing market needs and solving problems, they drive competition and improve the quality of goods and services. Additionally, successful ventures can attract investment and foster entrepreneurship, further boosting the economy.
4. Challenges Faced by Economic Ventures
Running an economic venture is not without challenges. Common obstacles include market competition, financial constraints, regulatory compliance, and technological disruptions. Entrepreneurs must also navigate uncertainties, such as changing consumer preferences and economic fluctuations, to ensure long-term sustainability.
See Also Who Are the Top Angels Investors Who Invest in Robotics Startups
Who Are the Top Angels Investors Who Invest in Robotics Startups5. Strategies for Success in Economic Ventures
To succeed, economic ventures must adopt effective strategies. These include market research, financial planning, innovation, and customer engagement. Building a strong brand, leveraging technology, and fostering a skilled workforce are also critical. Additionally, partnerships and collaborations can provide valuable resources and opportunities for growth.
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk-Taking | Involves uncertainty and potential for loss. |
| Investment | Requires allocation of resources like capital and labor. |
| Value Creation | Aims to meet market needs and generate profit. |
| Competition | Operates in a competitive market environment. |
| Innovation | Drives growth and differentiation in the market. |
What is the meaning of economic venture?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Venturecapital-2f7ba3a27d0545f682a6238ea6b16cb9.png)
Definition of Economic Venture
An economic venture refers to a business or project undertaken with the primary goal of generating financial profit or achieving economic growth. It involves investing resources such as capital, time, and effort into activities that are expected to yield returns. Economic ventures can range from small-scale startups to large corporate initiatives.
- It focuses on creating value through goods, services, or innovations.
- It often involves risk, as the outcomes are uncertain.
- It requires strategic planning and resource allocation.
Types of Economic Ventures
Economic ventures can be categorized into various types based on their scale, industry, and objectives. These include small businesses, large corporations, non-profit initiatives, and social enterprises.
- Small businesses: Often locally operated with limited resources.
- Large corporations: Involve significant capital and global operations.
- Non-profit initiatives: Focus on social impact rather than profit.
Key Characteristics of Economic Ventures
Economic ventures share several defining characteristics, such as profit orientation, risk-taking, and innovation. These features distinguish them from other types of projects or activities.
- Profit orientation: The primary goal is to generate revenue.
- Risk-taking: Ventures often involve uncertainty and potential losses.
- Innovation: Many ventures introduce new ideas or technologies.
Importance of Economic Ventures
Economic ventures play a crucial role in driving economic growth, creating employment opportunities, and fostering innovation. They contribute to the overall development of societies and economies.
- Economic growth: Ventures stimulate production and consumption.
- Employment opportunities: They create jobs for individuals.
- Innovation: Ventures often lead to technological advancements.
Challenges Faced by Economic Ventures
Despite their potential benefits, economic ventures often encounter challenges such as market competition, financial constraints, and regulatory hurdles. Overcoming these obstacles is essential for success.
- Market competition: Ventures must differentiate themselves to survive.
- Financial constraints: Limited funding can hinder growth.
- Regulatory hurdles: Compliance with laws and regulations is necessary.
What is an example of a venture?
An example of a venture is a startup company that develops and sells innovative tech products, such as a new mobile app or a software platform. This type of venture typically involves high risk but also the potential for high rewards if the product succeeds in the market. Ventures can also include small businesses, joint ventures between companies, or even social enterprises aimed at solving community problems.
What is a Startup Venture?
A startup venture refers to a newly established business, often in the technology sector, that aims to bring a unique product or service to the market. These ventures are characterized by their innovative ideas and scalability potential. Key aspects include:
- High risk: Startups often operate in uncertain markets with unproven business models.
- Innovation: They focus on creating something new or improving existing solutions.
- Funding: Startups typically rely on external investments, such as venture capital or angel investors.
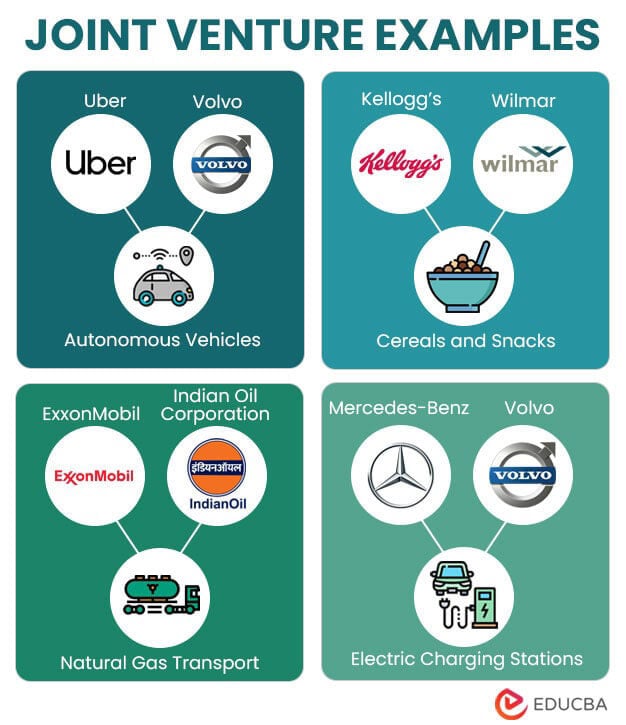
What is a Joint Venture?
A joint venture is a business arrangement where two or more parties collaborate to achieve a specific goal. This type of venture allows companies to share resources, expertise, and risks. Key features include:
- Shared ownership: Partners contribute assets and share profits or losses.
- Strategic goals: Joint ventures are often formed to enter new markets or develop new products.
- Limited duration: These ventures are usually temporary and dissolve once the goal is achieved.
A social venture is a business that prioritizes social impact over profit. These ventures aim to address societal issues, such as poverty, education, or environmental sustainability. Key characteristics include:
- Mission-driven: The primary goal is to create positive change in society.
- Revenue generation: Social ventures often generate income to sustain their operations.
- Scalability: Successful social ventures can expand their impact to broader communities.
What is a Small Business Venture?
A small business venture refers to a privately owned company that operates on a smaller scale compared to large corporations. These ventures are often local and serve niche markets. Key aspects include:
- Local focus: Small businesses typically cater to a specific community or region.
- Owner-operated: The business is usually managed by the owner or a small team.
- Flexibility: Small businesses can adapt quickly to market changes and customer needs.
What is a High-Risk Venture?
A high-risk venture is a business or project that involves significant uncertainty and potential for failure. These ventures often require substantial investment and have a higher chance of not succeeding. Key features include:
- Uncertain outcomes: The success of the venture is not guaranteed.
- High rewards: If successful, the venture can yield substantial profits or breakthroughs.
- Innovation-driven: High-risk ventures often involve cutting-edge technology or untested markets.
What is the difference between a startup and a venture?

Definition and Core Concept
A startup is a newly established business, typically in its early stages, focused on developing a unique product or service to address a specific market need. Startups are often characterized by their innovative approach, scalability potential, and high-risk nature. On the other hand, a venture refers to a business undertaking or project, which can be a startup or an established company, aimed at achieving specific goals, often involving investment and risk.
- Startups are usually in the early stages of development.
- Ventures can include both new and established businesses.
- Both involve risk but differ in scope and structure.
Funding and Investment
Startups often rely on external funding sources such as angel investors, venture capitalists, or crowdfunding to fuel their growth. Ventures, however, may be self-funded or backed by larger corporations, depending on their nature and objectives.
- Startups seek funding to scale quickly.
- Ventures may have diverse funding sources.
- Investment strategies differ based on the business model.
Growth and Scalability
Startups are designed for rapid growth and scalability, often targeting large markets with innovative solutions. Ventures, while they may also aim for growth, can include projects with limited scope or specific objectives that do not require scaling.
- Startups prioritize scalability and market expansion.
- Ventures may focus on niche markets or specific goals.
- Growth strategies vary based on the business type.
Risk and Uncertainty
Startups are inherently risky due to their unproven business models and reliance on innovation. Ventures, depending on their nature, may carry varying levels of risk, with some being more stable and others equally uncertain.
- Startups face high uncertainty and failure rates.
- Ventures can range from low to high risk.
- Risk management approaches differ between the two.
Timeframe and Objectives
Startups often operate with a long-term vision, aiming to disrupt industries or create new markets. Ventures, however, may have shorter-term objectives, such as completing a specific project or achieving a particular milestone.
- Startups focus on long-term innovation and market impact.
- Ventures may have defined, short-term goals.
- Objectives align with the nature of the business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an economic venture?
An economic venture refers to any activity or project undertaken with the primary goal of generating financial profit or achieving economic growth. This can include starting a new business, investing in existing enterprises, or launching innovative products or services. The success of an economic venture often depends on factors such as market demand, effective management, and strategic planning. It plays a crucial role in driving economic development and creating opportunities for individuals and communities.
What are the key characteristics of an economic venture?
The key characteristics of an economic venture include a clear profit motive, a well-defined business plan, and a focus on value creation. These ventures often involve risk-taking, as they require investment of resources such as time, money, and effort. Additionally, they aim to address a specific market need or solve a problem, which helps ensure their sustainability. Innovation and adaptability are also essential traits, as they allow the venture to thrive in competitive environments.
How does an economic venture differ from a non-profit initiative?
An economic venture differs from a non-profit initiative primarily in its purpose and financial structure. While economic ventures are driven by the goal of generating profit and maximizing returns for stakeholders, non-profit initiatives focus on achieving social, cultural, or environmental objectives without the intention of making a profit. Economic ventures rely on revenue from sales, investments, or services, whereas non-profits often depend on donations, grants, or fundraising to sustain their operations.
What are some examples of successful economic ventures?
Examples of successful economic ventures include companies like Apple, which revolutionized the technology industry with innovative products, and Amazon, which transformed e-commerce and logistics. Startups such as Uber and Airbnb are also notable examples, as they disrupted traditional industries by introducing new business models. These ventures demonstrate the importance of innovation, scalability, and customer-centric strategies in achieving long-term success and economic impact.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles