LLC Operating Agreement: Ohio
An LLC operating agreement is a foundational document that outlines the structure, management, and operational guidelines for a limited liability company in Ohio. While Ohio law does not legally require LLCs to adopt an operating agreement, creating one is strongly recommended to establish clear expectations among members, define roles and responsibilities, and safeguard the company’s limited liability status. This customizable contract addresses critical aspects such as profit distribution, decision-making processes, dispute resolution, and procedures for adding or removing members. A well-drafted operating agreement not only ensures compliance with state regulations but also provides a framework for mitigating conflicts and maintaining operational clarity as the business evolves.
- Understanding the Importance of an LLC Operating Agreement in Ohio
- Is an operating agreement required for LLC in Ohio?
- Can I write my own operating agreement for my LLC?
- What are the pitfalls of an LLC operating agreement?
- What if an LLC has no operating agreement?
- Frequently Asked Questions About LLCs (FAQs)
Understanding the Importance of an LLC Operating Agreement in Ohio
Key Provisions of an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement
An LLC Operating Agreement in Ohio outlines the internal structure, management, and financial operations of the business. Essential provisions include member ownership percentages, profit and loss distribution, voting rights, and management structure (member-managed vs. manager-managed). The agreement should also address dispute resolution, dissolution procedures, and rules for admitting new members. While Ohio does not legally require an LLC to have an operating agreement, creating one ensures clarity and legal protection.
See AlsoArizona LLC Operating Agreement| Provision | Description |
| Member Ownership | Defines ownership stakes and capital contributions. |
| Management Structure | Specifies if members or appointed managers control operations. |
| Profit Distribution | Details how profits/losses are allocated among members. |
| Dissolution Terms | Outlines conditions for dissolving the LLC. |
Ohio State Requirements for LLC Operating Agreements
Ohio law (Chapter 1705 of the Ohio Revised Code) does not mandate filing an operating agreement with the state. However, the agreement must comply with state regulations, such as permitting single-member LLCs and allowing oral or written agreements. Key requirements include adhering to fiduciary duties of members, avoiding illegal activities, and ensuring the agreement does not override statutory defaults unless explicitly stated.
| Requirement | Details |
| Single-Member LLCs | Allowed under Ohio law. |
| Oral Agreements | Permitted but not recommended for clarity. |
| Fiduciary Duties | Members must act in the LLC’s best interest. |
Roles and Responsibilities of Members in an Ohio LLC
Members in an Ohio LLC can be active participants (managing daily operations) or passive investors. The operating agreement should define their voting power, financial obligations, and liability limitations. For manager-managed LLCs, non-managing members have no operational authority unless specified. All members must adhere to confidentiality clauses and non-compete agreements if included.
See Also Are There Any Venture Capital Firms That Invest in Retail Businesses
Are There Any Venture Capital Firms That Invest in Retail Businesses| Role | Responsibilities |
| Managing Member | Oversees operations, finances, and legal compliance. |
| Non-Managing Member | Provides capital but has no operational control. |
| Voting Rights | Determined by ownership percentage or agreement terms. |
Amending an LLC Operating Agreement in Ohio
To amend an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement, unanimous consent is typically required unless the original agreement specifies a lower threshold. Amendments must be documented in writing and signed by all members. Common reasons for amendments include adding/removing members, changing profit-sharing ratios, or updating management roles.
| Step | Process |
| Proposal | A member suggests changes to the agreement. |
| Voting Threshold | Majority or unanimous approval as per original terms. |
| Documentation | Revised agreement is signed and stored with LLC records. |
How Ohio LLC Operating Agreements Differ from Other States
Unlike states like Delaware or California, Ohio does not require operating agreements to be filed with the Secretary of State. Additionally, Ohio allows oral agreements, whereas states like Florida mandate written agreements. Tax treatment and default rules (e.g., dissolution triggers) may also vary.
See AlsoConnecticut LLC Operating Agreement| Aspect | Ohio | Other States |
| Filing Requirement | Not required | Required in some states (e.g., Missouri). |
| Oral Agreements | Permitted | Often invalid (e.g., New York). |
| Default Management | Member-managed | Varies (e.g., Texas defaults to manager-managed). |
Is an operating agreement required for LLC in Ohio?

Is an Operating Agreement Legally Required for an LLC in Ohio?
In Ohio, an operating agreement is not legally required to form or operate an LLC. The state does not mandate LLCs to have this document. However, it is highly recommended to create one to establish clear rules, protect the business structure, and avoid disputes among members.
See Also What Are Examples of Vc Due Diligence Check Lists?
What Are Examples of Vc Due Diligence Check Lists?- No statutory requirement: Ohio law (Chapter 1705 of the Ohio Revised Code) does not require LLCs to adopt an operating agreement.
- Flexibility: Members can customize the agreement to suit their business needs.
- Legal protection: Without an agreement, default state laws govern the LLC, which may not align with members' intentions.
Why Should an Ohio LLC Consider an Operating Agreement?
Even though Ohio does not require an operating agreement, having one provides legal clarity, financial security, and operational guidelines for the LLC. It helps prevent misunderstandings and ensures smooth business operations.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clarifies management structure, voting rights, and profit-sharing.
- Protect limited liability status: Courts may disregard the LLC’s liability protection without a formal agreement.
- Resolve disputes: Outlines procedures for handling member disagreements or exit strategies.
What Happens If an Ohio LLC Operates Without an Agreement?
Operating without an agreement means the LLC is governed by default state laws, which may not reflect the members’ preferences. This can lead to complications in management, profit distribution, and decision-making.
- State default rules apply: Ohio’s LLC statutes dictate procedures for dissolution, member withdrawals, and more.
- Unclear financial terms: Profit splits and capital contributions may default to equal shares, regardless of initial investments.
- Increased litigation risk: Disputes may require court intervention without predefined resolutions.
How to Create an Operating Agreement for an Ohio LLC
Drafting an operating agreement involves outlining the LLC’s management structure, financial arrangements, and operational procedures. While Ohio does not require filing the document, it should be signed by all members and stored securely.
- Define membership details: Names, ownership percentages, and capital contributions.
- Establish management rules: Member-managed vs. manager-managed structures.
- Include dissolution terms: Steps for winding down the LLC if necessary.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement
Errors in an operating agreement can undermine its effectiveness. Ensure the document is comprehensive, legally sound, and regularly updated to reflect changes in the business or membership.
- Omitting dispute resolution clauses: Failing to outline mediation or arbitration processes.
- Ignoring tax provisions: Clarify how profits/losses are reported to the IRS.
- Not updating the agreement: Revise it when membership changes or the business scales.
Can I write my own operating agreement for my LLC?

Yes, you can write your own operating agreement for your LLC. Most states do not legally require an operating agreement, but drafting one is highly recommended to establish ownership structure, management roles, and operational rules. However, while creating your own agreement offers flexibility and cost savings, it must comply with your state’s LLC laws. Inadequate clauses or omissions could lead to disputes or legal vulnerabilities. Consulting a legal professional is advisable for complex situations, but a self-drafted agreement is feasible for straightforward LLCs with clear member expectations.
Benefits of Drafting Your Own LLC Operating Agreement
Customization and cost efficiency are primary advantages of writing your own operating agreement. Tailoring the document ensures it aligns precisely with your business’s needs, unlike generic templates.
- Control over terms: Define profit-sharing, voting rights, and dissolution procedures.
- Lower expenses: Avoid attorney fees for simple agreements.
- Clarity: Members gain a clear understanding of roles and obligations.
Legal Requirements for an LLC Operating Agreement
While states rarely mandate operating agreements, certain legal standards must be met to ensure enforceability. Key elements include compliance with state laws and inclusion of essential provisions.
- State compliance: Adhere to your state’s LLC statutes (e.g., California’s Corporations Code).
- Member details: Clearly list members’ names, contributions, and ownership percentages.
- Dispute resolution: Outline processes for resolving conflicts to avoid litigation.
How to Customize Your Operating Agreement
A personalized operating agreement should reflect your LLC’s unique operational structure and long-term goals. Focus on adaptable clauses to accommodate future changes.
- Management structure: Specify whether the LLC is member-managed or manager-managed.
- Amendment process: Define how modifications to the agreement will be approved.
- Exit strategies: Include buyout rules or procedures for member withdrawal.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Self-Drafted Operating Agreement
Overlooking critical details or using ambiguous language can render your agreement ineffective or legally risky.
- Vagueness: Avoid unclear terms about profit distribution or decision-making.
- Ignoring state laws: Failing to incorporate mandatory state-specific clauses.
- Omitting dissolution terms: Not planning for business closure or member exits.
When to Consult an Attorney for Your Operating Agreement
While DIY agreements work for simple LLCs, complex scenarios warrant professional legal advice.
- Multi-member disputes: Anticipate disagreements among owners with differing interests.
- Unusual structures: Complex ownership tiers or foreign business operations.
- Regulatory compliance: Industries with strict regulations (e.g., healthcare, finance).
What are the pitfalls of an LLC operating agreement?
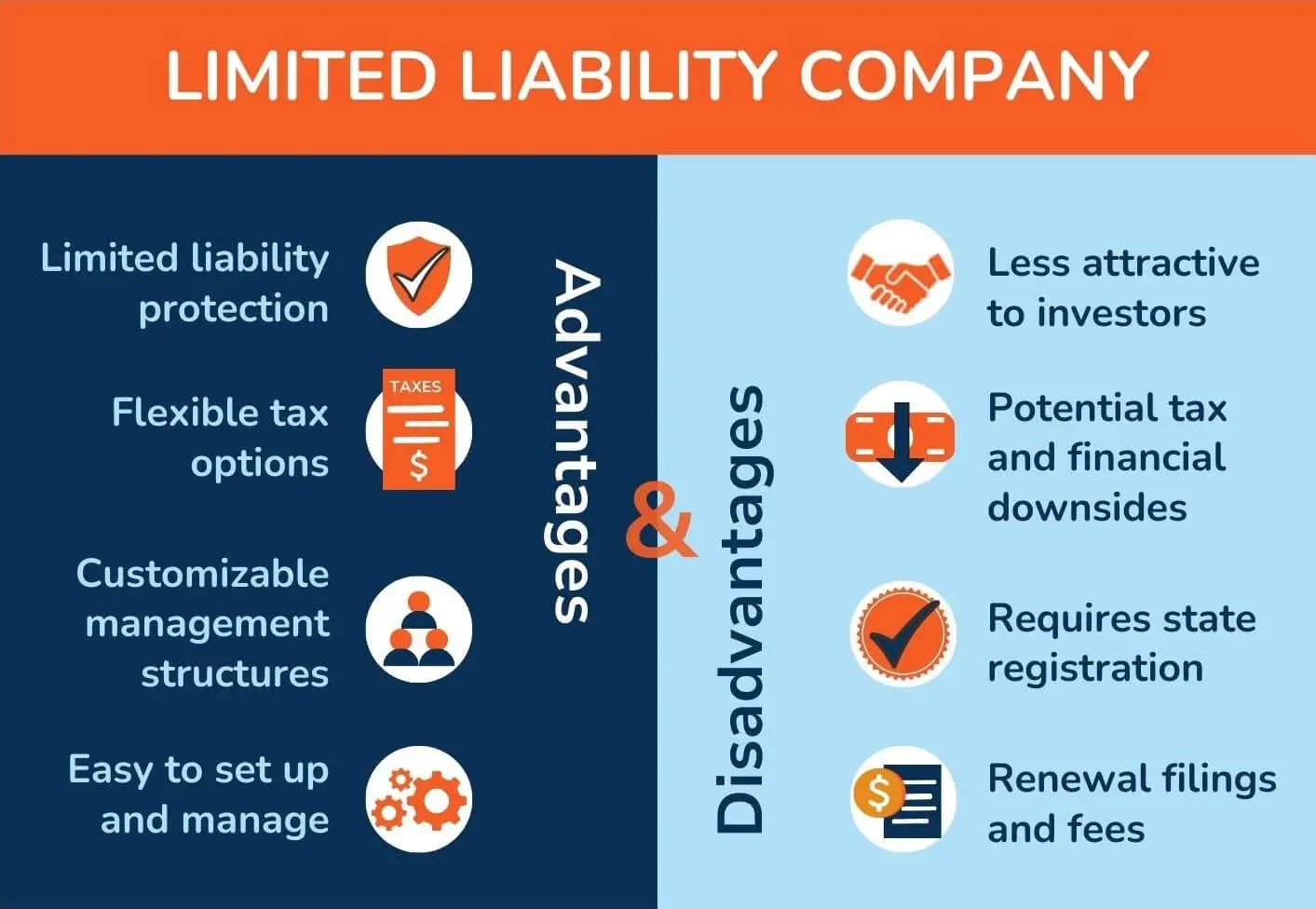
Inadequate Definition of Management Roles and Responsibilities
A poorly defined management structure in an LLC operating agreement can lead to confusion, power struggles, and operational inefficiencies. Without explicit roles, members may disagree over decision-making authority or day-to-day responsibilities.
- Unclear voting rights may result in deadlocks during critical decisions.
- Mixing manager-managed and member-managed roles without clarity can cause role overlap.
- Failure to outline succession plans for key roles disrupts continuity during transitions.
Unclear Profit and Loss Distribution Terms
Ambiguity in profit-sharing or loss allocation often sparks disputes among members, especially if contributions or workloads vary. The operating agreement must specify formulas or percentages to avoid financial conflicts.
- Using arbitrary percentages instead of contribution-based calculations creates inequity.
- Ignoring capital account maintenance complicates tax reporting.
- Omitting provisions for silent partners or investors leads to misaligned expectations.
Failure to Address Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Without predefined methods to resolve conflicts, disagreements can escalate into costly litigation or dissolve the LLC entirely. A robust agreement outlines steps for mediation or buyouts.
- Missing mediation clauses forces reliance on courts.
- No buy-sell agreements for member exits prolongs disputes.
- Ignoring deadlock-breaking procedures halts operations during stalemates.
Overlooking Amendments and Updates to the Agreement
An inflexible operating agreement risks becoming obsolete as the LLC evolves. Failing to establish clear amendment processes stifles adaptability.
- Requiring unanimous consent for changes makes updates impractical.
- Not addressing tax law changes or industry shifts leaves the LLC vulnerable.
- Ignoring member additions/removals complicates ownership transitions.
Insufficient Provisions for Member Exit or Dissolution
Vague exit strategies or dissolution terms can paralyze the LLC if a member leaves or the business closes. Clear protocols ensure smooth transitions.
- No buyout valuation methods lead to price disputes during exits.
- Ignoring bankruptcy scenarios creates legal ambiguities.
- Failing to outline asset distribution steps prolongs dissolution.
What if an LLC has no operating agreement?

What Happens If an LLC Operates Without an Operating Agreement?
If an LLC lacks an operating agreement, it will default to the state’s default LLC laws. These laws vary by jurisdiction but generally provide a one-size-fits-all framework that may not align with the members’ intentions. Without a customized agreement, critical aspects like profit distribution, management structure, and dispute resolution are left to statutory rules, potentially leading to conflicts or inefficiencies.
Default State Laws Govern the LLC
When there is no operating agreement, the LLC is subject to default state statutes under the jurisdiction where it was formed. These laws outline basic rules for governance but lack specificity.
- States like California and New York impose mandatory provisions for profit splits (e.g., equal shares unless otherwise stated).
- Management decisions default to member voting per capita, which may not reflect ownership stakes.
- Dissolution or member exit rules may force unwanted outcomes, such as dissolving the LLC if a member departs.
Unclear Member Roles and Responsibilities
Without an operating agreement, member roles and obligations remain undefined, creating ambiguity in daily operations.
- No clear designation of managers vs. passive members, leading to confusion over decision-making authority.
- Lack of guidelines for capital contributions or workload expectations.
- Potential disputes over fiduciary duties or conflicts of interest.
Profit and Loss Distribution Disputes
The absence of an operating agreement often results in disagreements over financial allocations.
- Profits and losses may be distributed equally by default, even if members contributed unevenly.
- No provisions for tax distributions or reinvestment strategies.
- Members cannot easily adjust distributions to reflect changing contributions or priorities.
Decision-Making and Voting Deadlocks
Without predefined rules, voting procedures and decision-making processes may stall.
- Unclear voting thresholds for major decisions (e.g., mergers, asset sales).
- Risk of deadlocks if members disagree on critical issues.
- No framework for resolving disputes or mediating conflicts.
Vulnerability in Legal and Financial Protections
An operating agreement strengthens an LLC’s liability protections and legal standing.
- Courts may disregard corporate veil protections if the LLC appears disorganized.
- No documented processes for admitting new members or handling member exits.
- Increased exposure to lawsuits due to ambiguous governance practices.
Frequently Asked Questions About LLCs (FAQs)
Is an LLC Operating Agreement required for Ohio LLCs?
Ohio does not legally require LLCs to have an Operating Agreement. However, creating one is highly recommended to establish clear rules for ownership, management, and operations. Without an Operating Agreement, your LLC will default to Ohio’s default state laws, which may not align with your business goals. This document also helps protect limited liability status by demonstrating a formal separation between personal and business affairs.
What key provisions should an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement include?
A comprehensive Ohio LLC Operating Agreement should outline member roles, profit/loss distribution, voting rights, and management structure (member-managed vs. manager-managed). It should also include procedures for adding/removing members, dispute resolution, and dissolution. Clauses addressing meeting requirements, capital contributions, and ownership transfer restrictions are equally critical to avoid future conflicts.
Can an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement be amended after formation?
Yes, an Ohio LLC Operating Agreement can be amended if members follow the amendment process outlined in the original document. Typically, amendments require a majority or supermajority vote of the members. Any changes should be documented in writing, signed by all members, and kept with the LLC’s official records to ensure legal enforceability.
Does a single-member Ohio LLC need an Operating Agreement?
While a single-member LLC is not obligated to have an Operating Agreement in Ohio, drafting one is still advisable. The agreement reinforces personal asset protection by formalizing the LLC’s separation from the owner’s finances. It also provides clarity on business structure, succession plans, and operational procedures, which can be valuable for taxes, loans, or future expansion.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles