How to Start or Launch a Venture Capital Firm or Vc Fund

Starting a venture capital (VC) firm or fund is an ambitious endeavor that requires a blend of financial expertise, industry knowledge, and strategic vision. Venture capital plays a pivotal role in fueling innovation by providing early-stage funding to startups with high growth potential. However, launching a VC firm involves more than just capital; it demands a deep understanding of market trends, risk assessment, and the ability to identify promising opportunities. This article explores the essential steps to establish a successful VC firm, from building a strong network and raising funds to structuring deals and managing portfolios, offering insights for aspiring venture capitalists ready to navigate this dynamic industry.
- How to Start or Launch a Venture Capital Firm or VC Fund
- How much money is needed to start a venture capital firm?
- What is the 80/20 rule in venture capital?
- What is the difference between a VC firm and a VC fund?
- Do you need a license to start a venture capital firm?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to Start or Launch a Venture Capital Firm or VC Fund
Starting a venture capital (VC) firm or fund is a complex but rewarding endeavor that requires a combination of financial expertise, industry knowledge, and a strong network. Below, we break down the key steps and considerations to help you navigate this process effectively.
See Also How Do I Start a Venture Capital Firm in Canada?
How Do I Start a Venture Capital Firm in Canada?1. Understanding the Venture Capital Landscape
Before diving into the creation of a VC firm, it’s crucial to understand the venture capital ecosystem. Venture capital involves investing in early-stage or high-growth companies with significant potential. This type of investment is high-risk but can yield substantial returns. Familiarize yourself with the different stages of funding, such as seed rounds, Series A, Series B, and beyond. Additionally, research the industries or sectors where VC activity is most prominent, such as technology, biotech, or clean energy.
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Stages of Funding | Seed, Series A, Series B, etc. |
| High-Risk Investments | Focus on startups with high growth potential. |
| Industry Focus | Tech, biotech, clean energy, etc. |
2. Building a Strong Network
A successful VC firm relies heavily on a robust network of entrepreneurs, investors, and industry experts. Start by attending industry events, joining startup incubators, and connecting with key players in your target sectors. Building relationships with founders and other investors will not only help you source deals but also provide valuable insights into market trends and opportunities. Consider leveraging platforms like LinkedIn or AngelList to expand your reach.
See Also How Do Vc Firms Raise Their Funds?
How Do Vc Firms Raise Their Funds?| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Entrepreneur Network | Connect with founders and startups. |
| Investor Network | Collaborate with other VC firms and angel investors. |
| Industry Events | Attend conferences and pitch events. |
3. Securing Capital for Your Fund
Raising capital is one of the most critical steps in launching a VC fund. You’ll need to convince limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, family offices, or high-net-worth individuals, to commit funds to your venture. Prepare a compelling pitch deck that outlines your investment thesis, track record (if any), and the potential returns for investors. Be transparent about your fee structure, typically consisting of a management fee (1-2% of assets under management) and a carried interest (20% of profits).
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Limited Partners (LPs) | Institutional investors, family offices, etc. |
| Pitch Deck | Highlight investment thesis and potential returns. |
| Fee Structure | Management fee and carried interest. |
4. Developing an Investment Strategy
Your investment strategy will define how your VC firm operates and what types of companies you target. Decide whether you’ll focus on early-stage startups, growth-stage companies, or a mix of both. Establish clear criteria for evaluating potential investments, such as market size, team expertise, and product scalability. Additionally, consider whether you’ll specialize in a specific industry or adopt a more diversified approach.
See Also How to Start a Micro Vc Fund
How to Start a Micro Vc Fund| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage Focus | Early-stage, growth-stage, or both. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Market size, team expertise, scalability. |
| Industry Specialization | Tech, healthcare, fintech, etc. |
5. Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Launching a VC fund involves navigating a complex legal and regulatory landscape. You’ll need to set up the appropriate legal structure for your firm, such as a limited partnership (LP) or limited liability company (LLC). Ensure compliance with securities laws, including filing the necessary documents with regulatory bodies like the SEC in the U.S. It’s also essential to draft clear limited partnership agreements (LPAs) that outline the terms and conditions for your investors.
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Legal Structure | LP, LLC, or other entities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | SEC filings and securities laws. |
| Limited Partnership Agreements | Define terms for investors. |
How much money is needed to start a venture capital firm?

 Where Can You Find Reviews and Ratings for Angel Investors and Venture Capital Firms
Where Can You Find Reviews and Ratings for Angel Investors and Venture Capital FirmsInitial Capital Requirements for a Venture Capital Firm
Starting a venture capital firm requires a significant amount of capital, typically ranging from $10 million to $100 million or more, depending on the scale and focus of the firm. This capital is used to invest in startups and early-stage companies, as well as to cover operational expenses. Below are the key factors influencing the initial capital requirements:
- Fund Size: The amount of money raised from limited partners (LPs) determines the firm's investment capacity. Larger funds require more capital upfront.
- Operational Costs: Salaries, office space, legal fees, and other administrative expenses must be covered, often requiring a reserve of 2-3% of the total fund size.
- Deal Flow and Diversification: A larger fund allows for more investments and diversification across industries, reducing risk.
Sources of Funding for Venture Capital Firms
Venture capital firms typically raise funds from institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and family offices. These sources provide the necessary capital to establish and operate the firm. Key sources include:
See AlsoWhat Are the Best Venture Capital Newsletters?- Institutional Investors: Pension funds, endowments, and insurance companies are common contributors.
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: Wealthy individuals often invest in venture capital firms to gain access to high-growth opportunities.
- Family Offices: These entities manage the wealth of affluent families and are increasingly investing in venture capital.
Legal and Regulatory Costs
Establishing a venture capital firm involves significant legal and regulatory expenses. These costs include forming the fund structure, compliance with securities laws, and drafting partnership agreements. Key expenses include:
- Legal Fees: Drafting fund documents and ensuring compliance can cost between $50,000 and $200,000.
- Registration Fees: Registering with regulatory bodies like the SEC incurs additional costs.
- Ongoing Compliance: Maintaining compliance with regulations requires continuous investment in legal and administrative resources.
Operational Expenses of a Venture Capital Firm
Running a venture capital firm involves ongoing operational costs, which must be factored into the initial capital requirements. These expenses include:
- Salaries: Hiring experienced investment professionals and support staff is essential but costly.
- Office Space: Physical office space in major financial hubs can be expensive.
- Technology and Tools: Investment in software for deal flow management, portfolio tracking, and communication is necessary.
Risk Management and Reserves
Venture capital firms must allocate a portion of their capital to manage risks and unforeseen expenses. This includes setting aside reserves for follow-on investments and operational contingencies. Key considerations include:
- Follow-On Investments: Reserving capital for subsequent funding rounds in portfolio companies is crucial.
- Operational Reserves: Maintaining a buffer for unexpected costs ensures the firm's sustainability.
- Diversification: Allocating funds across multiple sectors and stages reduces the risk of concentrated losses.
What is the 80/20 rule in venture capital?

The 80/20 rule in venture capital refers to the observation that a small percentage of investments (typically around 20%) generate the majority of returns (around 80%). This principle, also known as the Pareto Principle, highlights the uneven distribution of outcomes in venture capital portfolios. Investors expect that most startups will fail or underperform, while a few will achieve outsized success, driving the overall profitability of the fund.
Understanding the 80/20 Rule in Venture Capital
The 80/20 rule is a guiding principle for venture capitalists to manage risk and focus on high-potential investments. It emphasizes the importance of identifying and nurturing the top-performing startups in a portfolio. Key points include:
- Portfolio diversification: Investors spread capital across multiple startups to mitigate risk.
- Focus on outliers: A small number of startups are expected to deliver exponential returns.
- Risk management: Accepting that most investments may fail while relying on a few to succeed.
Why the 80/20 Rule Matters in Venture Capital
The 80/20 rule is critical because it aligns with the high-risk, high-reward nature of venture capital. It helps investors:
- Set realistic expectations: Understand that not all startups will succeed.
- Allocate resources effectively: Prioritize support for startups with the highest growth potential.
- Measure success: Evaluate portfolio performance based on the returns from top-performing investments.
How Venture Capitalists Apply the 80/20 Rule
Venture capitalists use the 80/20 rule to guide their investment strategies. This involves:
- Identifying high-potential startups: Conducting thorough due diligence to spot outliers.
- Providing strategic support: Offering mentorship, networks, and resources to top-performing startups.
- Exiting at the right time: Selling stakes in successful startups to maximize returns.
Challenges of the 80/20 Rule in Venture Capital
While the 80/20 rule is widely accepted, it comes with challenges such as:
- Identifying outliers: Predicting which startups will succeed is inherently uncertain.
- Balancing risk: Over-reliance on a few startups can be risky if they fail.
- Managing expectations: Limited partners may expect consistent returns, which is difficult in venture capital.
Examples of the 80/20 Rule in Action
The 80/20 rule is evident in many successful venture capital portfolios. Examples include:
- Sequoia Capital: Investments in companies like Apple and Google generated massive returns.
- Andreessen Horowitz: Backing startups like Airbnb and Lyft, which delivered significant profits.
- Accel Partners: Early investment in Facebook, which became a major success.
What is the difference between a VC firm and a VC fund?
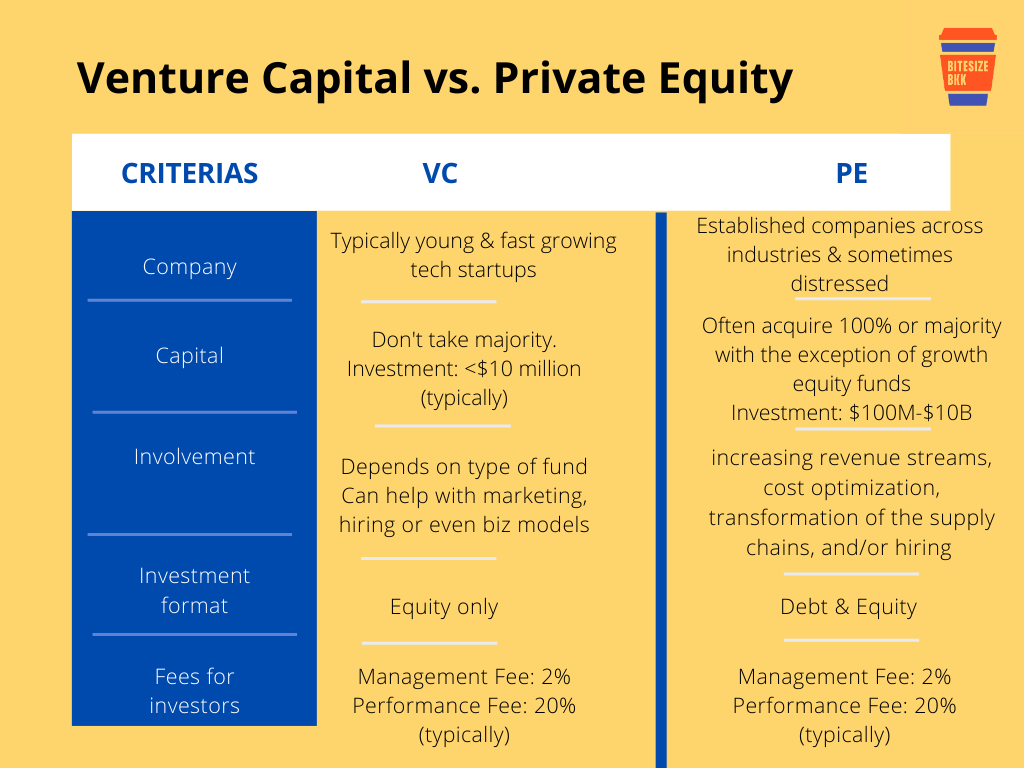
What is a VC Firm?
A VC firm is an organization that manages and operates venture capital investments. It is responsible for sourcing deals, conducting due diligence, and providing strategic guidance to portfolio companies. The firm is typically composed of experienced professionals, including general partners, who make investment decisions and manage the funds.
- Structure: A VC firm is a business entity that employs professionals to manage venture capital activities.
- Role: It identifies investment opportunities, negotiates terms, and supports portfolio companies.
- Management: The firm oversees multiple funds and ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
What is a VC Fund?
A VC fund is a pool of capital raised from investors, such as institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and corporations. This fund is managed by the VC firm and is used to invest in startups and high-growth companies. Each fund has a specific investment thesis, target industries, and geographic focus.
- Capital Pool: A VC fund is a collection of money raised from limited partners (LPs) for investment purposes.
- Investment Focus: It has a defined strategy, such as early-stage or growth-stage investments.
- Lifecycle: The fund operates for a fixed period, usually 10 years, after which it is liquidated, and returns are distributed to investors.
Key Differences Between a VC Firm and a VC Fund
The primary distinction lies in their roles and structures. A VC firm is the entity managing the investments, while a VC fund is the financial vehicle used to make those investments. The firm operates multiple funds over time, each with its own strategy and lifecycle.
- Entity vs. Vehicle: The firm is the management entity, while the fund is the investment vehicle.
- Scope: A firm can manage multiple funds simultaneously, each with different objectives.
- Responsibilities: The firm handles operations, while the fund provides the capital for investments.
How VC Firms and VC Funds Work Together
VC firms and VC funds are interdependent. The firm raises capital from investors to create a fund, which it then uses to invest in startups. The firm earns management fees and a share of the profits (carried interest) from the fund's performance.
- Capital Raising: The firm raises money from LPs to establish a fund.
- Investment Execution: The firm uses the fund to make investments in line with its strategy.
- Profit Sharing: The firm earns fees and a percentage of the fund's profits.
Examples of VC Firms and Their Funds
Prominent VC firms like Sequoia Capital and Andreessen Horowitz manage multiple funds. For instance, Sequoia Capital operates funds like Sequoia Capital Global Growth Fund and Sequoia Capital China Growth Fund, each targeting different markets and stages of investment.
- Sequoia Capital: Manages funds focused on global and regional markets.
- Andreessen Horowitz: Operates funds targeting early-stage and growth-stage startups.
- Accel: Runs funds specializing in technology and software investments.
Do you need a license to start a venture capital firm?

Is a License Required to Start a Venture Capital Firm?
In most jurisdictions, you do not need a specific license to start a venture capital firm. However, there are regulatory requirements and compliance obligations that must be met. These vary depending on the country or state where the firm is established. For example, in the United States, venture capital firms often need to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as investment advisors if they manage a certain amount of assets.
- Check local regulations to determine if registration is required.
- Ensure compliance with securities laws and anti-money laundering rules.
- Consult legal and financial advisors to navigate the regulatory landscape.
What Are the Regulatory Requirements for Venture Capital Firms?
Venture capital firms must adhere to specific regulatory requirements to operate legally. These include registering with relevant authorities, such as the SEC in the U.S., and complying with securities laws. Additionally, firms must follow anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations to prevent illegal activities.
- Register with the appropriate regulatory body in your jurisdiction.
- Implement AML and KYC procedures to ensure compliance.
- Regularly audit your operations to maintain regulatory standards.
Do Venture Capital Firms Need to Register with the SEC?
In the United States, venture capital firms may need to register with the SEC if they manage assets above a certain threshold. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, firms managing over $150 million in assets must register as investment advisors. However, smaller firms may qualify for exemptions.
- Determine if your firm meets the SEC's asset threshold for registration.
- Understand the exemptions available for smaller venture capital firms.
- File the necessary paperwork and pay registration fees if required.
What Legal Structures Are Available for Venture Capital Firms?
Venture capital firms can adopt various legal structures, such as limited partnerships (LPs), limited liability companies (LLCs), or corporations. The choice of structure depends on factors like liability protection, tax implications, and investor preferences. For example, LPs are commonly used because they offer liability protection for limited partners.
- Choose a legal structure that aligns with your firm's goals and investor needs.
- Consult a legal expert to understand the tax and liability implications.
- Draft partnership agreements or operating agreements to formalize the structure.
How to Ensure Compliance with Securities Laws?
Compliance with securities laws is critical for venture capital firms. This includes adhering to regulations like the Securities Act of 1933 and the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. Firms must also ensure that all fundraising activities, such as issuing private placements, comply with exemptions like Regulation D.
- Familiarize yourself with key securities laws and regulations.
- Ensure all fundraising activities comply with exemptions like Regulation D.
- Work with legal counsel to review and update compliance policies regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key steps to start a venture capital firm?
Starting a venture capital firm involves several critical steps. First, you need to define your investment thesis, which outlines the types of startups or industries you plan to focus on. Next, you must secure capital commitments from limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, family offices, or high-net-worth individuals. After raising funds, you'll need to establish a legal structure for your firm, typically a limited partnership (LP) or limited liability company (LLC). Finally, build a strong team with expertise in deal sourcing, due diligence, and portfolio management to ensure the success of your fund.
How much capital is required to launch a VC fund?
The amount of capital required to launch a VC fund varies depending on your goals and target market. Typically, a first-time fund ranges from $10 million to $50 million, but larger funds can require hundreds of millions. The capital is used to invest in startups and cover operational expenses, such as salaries, legal fees, and office costs. It's essential to have a clear plan for how much you need to raise and how you'll allocate it to ensure your fund's sustainability and ability to generate returns for your investors.
What are the legal and regulatory requirements for starting a VC firm?
Starting a VC firm involves navigating various legal and regulatory requirements. You'll need to register your firm with the appropriate regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. Additionally, you must comply with securities laws when raising funds from investors. Drafting a limited partnership agreement (LPA) is crucial, as it outlines the terms of the fund, including management fees, carried interest, and investor rights. Consulting with legal and financial experts is highly recommended to ensure compliance and avoid potential pitfalls.
How do you attract investors to a new VC fund?
Attracting investors to a new VC fund requires a combination of a compelling investment strategy, a strong track record, and effective networking. Start by crafting a clear and persuasive pitch deck that highlights your fund's unique value proposition, target market, and expected returns. Leverage your professional network to connect with potential limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, family offices, and high-net-worth individuals. Building trust and demonstrating your expertise in the startup ecosystem are key to securing commitments. Additionally, offering transparency and regular updates to investors can help establish long-term relationships.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles