What Are the Requirements to Be Considered a Venture Capitalist
Venture capitalists play a pivotal role in the startup ecosystem, providing not only financial backing but also strategic guidance to emerging companies. However, becoming a venture capitalist is not a straightforward path and requires a unique combination of skills, experience, and resources. This article explores the essential requirements to be considered a venture capitalist, from educational background and industry expertise to networking capabilities and access to capital. Whether you are an aspiring investor or simply curious about the venture capital world, understanding these prerequisites can shed light on what it takes to succeed in this competitive and high-stakes field.
What Are the Requirements to Be Considered a Venture Capitalist?
1. Strong Financial Background
To be considered a venture capitalist, having a strong financial background is essential. This typically includes experience in investment banking, private equity, or corporate finance. A deep understanding of financial modeling, valuation techniques, and market analysis is crucial. Many venture capitalists also hold advanced degrees such as an MBA or CFA certification, which provide the necessary knowledge and credibility in the field.
See AlsoWhat Qualifications Do You Need to Become a Venture Capitalist?2. Extensive Industry Knowledge
Venture capitalists must possess extensive industry knowledge to identify promising startups and assess their potential. This involves staying updated on emerging trends, technological advancements, and market dynamics. A successful venture capitalist often specializes in specific sectors, such as technology, healthcare, or clean energy, allowing them to make informed investment decisions.
3. Robust Network of Contacts
A robust network of contacts is a key requirement for venture capitalists. Building relationships with entrepreneurs, other investors, and industry experts can provide access to lucrative investment opportunities. Networking also helps in due diligence and portfolio management, as it allows venture capitalists to gather insights and support for their investments.
See AlsoWhat is the Difference Between Vc Angel Investor and Acceleration Programs and How Do They Help a Start Up4. Risk Management Skills
Venture capitalists must have strong risk management skills to navigate the high-risk, high-reward nature of startup investments. This involves diversifying portfolios, conducting thorough due diligence, and monitoring investments closely. The ability to assess risks and make calculated decisions is critical to achieving long-term success in venture capital.
5. Proven Track Record
A proven track record of successful investments is often a prerequisite for becoming a venture capitalist. This demonstrates the ability to identify high-potential startups, provide strategic guidance, and generate significant returns. Many venture capitalists start their careers by working in investment firms or accelerators to build their reputation and experience.
See Also How Do Investment Banking Venture Capital and Private Equity Differ in Terms of Prestige
How Do Investment Banking Venture Capital and Private Equity Differ in Terms of Prestige| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Background | Experience in finance, advanced degrees, and certifications. |
| Industry Knowledge | Deep understanding of specific sectors and market trends. |
| Network of Contacts | Strong relationships with entrepreneurs, investors, and experts. |
| Risk Management | Ability to assess and mitigate investment risks. |
| Track Record | History of successful investments and strategic guidance. |
What qualifies you as a venture capitalist?

What is the Role of Experience in Venture Capital?
Experience is a critical factor in qualifying as a venture capitalist. It involves a deep understanding of the startup ecosystem, market trends, and investment strategies. Key aspects include:
See Also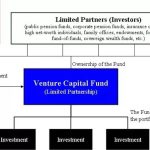 What is the Typical Structure of a Vc Fund?
What is the Typical Structure of a Vc Fund?- Years of involvement in the venture capital industry, which provides insights into successful and failed investments.
- Hands-on experience working with startups, helping them scale, and navigating challenges.
- Networking with other investors, entrepreneurs, and industry experts to stay informed and identify opportunities.
What Financial Expertise is Required?
Financial expertise is essential for evaluating potential investments and managing portfolios effectively. This includes:
- Analyzing financial statements to assess a startup's health and growth potential.
- Valuation skills to determine the worth of a company and negotiate favorable terms.
- Risk management to balance high-risk, high-reward investments with more stable opportunities.
How Important is Industry Knowledge?
Industry knowledge allows venture capitalists to identify promising sectors and startups. This involves:
See Also Which Are the Top Venture Capital Firms in Vancouver?
Which Are the Top Venture Capital Firms in Vancouver?- Staying updated on emerging technologies, market trends, and regulatory changes.
- Understanding the competitive landscape to spot unique opportunities.
- Leveraging domain expertise to provide strategic guidance to portfolio companies.
What Soft Skills are Necessary?
Soft skills are crucial for building relationships and making informed decisions. These include:
- Communication to effectively negotiate deals and mentor startups.
- Decision-making under pressure, especially when evaluating high-stakes investments.
- Adaptability to navigate the dynamic and unpredictable nature of the startup world.
What is the Importance of a Strong Track Record?
A strong track record demonstrates credibility and success in venture capital. Key elements include:
- Successful exits such as IPOs or acquisitions, which showcase the ability to generate returns.
- Portfolio performance highlighting consistent growth and profitability.
- Reputation within the industry, attracting high-quality deal flow and partnerships.
What are the criteria for a venture capitalist?

What is the Role of a Venture Capitalist?
A venture capitalist (VC) is an investor who provides capital to startups and small businesses with high growth potential in exchange for equity. Their role extends beyond funding, as they often provide strategic guidance, mentorship, and access to networks to help businesses scale. Key responsibilities include:
- Identifying high-potential startups with innovative ideas or disruptive technologies.
- Conducting due diligence to assess the viability and risks of the investment.
- Negotiating terms of investment, including equity stakes and valuation.
- Monitoring portfolio companies to ensure growth and profitability.
- Exiting investments through IPOs, acquisitions, or mergers to realize returns.
What Are the Key Criteria for Evaluating Startups?
Venture capitalists evaluate startups based on several critical factors to determine their potential for success. These criteria include:
- Market opportunity: The size and growth potential of the target market.
- Team expertise: The experience, skills, and track record of the founding team.
- Product or service innovation: The uniqueness and scalability of the offering.
- Traction and metrics: Evidence of customer adoption, revenue growth, or user engagement.
- Business model: The sustainability and profitability of the revenue strategy.
What Types of Industries Do Venture Capitalists Target?
Venture capitalists often focus on industries with high growth potential and disruptive innovation. Common sectors include:
- Technology: Software, artificial intelligence, and fintech.
- Healthcare: Biotech, medical devices, and digital health solutions.
- E-commerce: Online retail and marketplaces.
- Clean energy: Renewable energy and sustainability-focused startups.
- Consumer goods: Innovative products and direct-to-consumer brands.
What Are the Stages of Venture Capital Investment?
Venture capital investments are typically made in stages, each corresponding to a startup's growth phase. These stages include:
- Seed stage: Initial funding to develop a prototype or validate the concept.
- Early stage (Series A): Funding to scale operations and achieve product-market fit.
- Growth stage (Series B and C): Capital to expand market reach and optimize business processes.
- Late stage (Series D and beyond): Funding for scaling globally or preparing for an IPO.
- Exit stage: Liquidation of the investment through an IPO, acquisition, or merger.
What Are the Risks and Rewards of Venture Capital?
Venture capital involves significant risks but also offers substantial rewards for successful investments. Key aspects include:
- High failure rate: Many startups fail, leading to potential loss of capital.
- Long investment horizon: Returns may take several years to materialize.
- High returns: Successful investments can yield exponential returns.
- Portfolio diversification: Investing in multiple startups mitigates risk.
- Strategic influence: VCs can shape the direction of the companies they invest in.
Can a single person be a venture capitalist?

Can a Single Person Operate as a Venture Capitalist?
Yes, a single person can operate as a venture capitalist, but it requires significant resources, expertise, and a strategic approach. Unlike institutional venture capital firms, an individual venture capitalist typically invests their own capital or raises funds from a small network of investors. This approach is often referred to as an angel investor or solo venture capitalist. Key factors for success include:
- Capital Availability: A substantial amount of personal wealth is necessary to make meaningful investments in startups.
- Industry Expertise: Deep knowledge of specific industries helps in identifying high-potential startups and providing value beyond funding.
- Networking Skills: Building strong connections with entrepreneurs, other investors, and industry leaders is crucial for deal flow and co-investment opportunities.
What Are the Advantages of Being a Solo Venture Capitalist?
Operating as a solo venture capitalist offers several unique advantages, including flexibility and autonomy. Unlike institutional investors, a solo VC can make decisions quickly without the need for lengthy approval processes. Key advantages include:
- Decision-Making Speed: Ability to act swiftly on investment opportunities without bureaucratic delays.
- Personal Branding: Building a personal reputation as an investor can attract high-quality startups seeking funding.
- Direct Impact: Greater involvement in the success of portfolio companies through mentorship and strategic guidance.
What Are the Challenges Faced by Solo Venture Capitalists?
While there are benefits, being a solo venture capitalist also comes with significant challenges. These include limited resources and higher risk exposure. Key challenges are:
- Limited Capital: Compared to institutional funds, an individual may have less capital to diversify investments.
- Risk Concentration: Investing personal funds means bearing the full brunt of any losses.
- Time Constraints: Managing due diligence, negotiations, and portfolio management alone can be overwhelming.
How Can a Solo Venture Capitalist Build a Strong Portfolio?
Building a strong portfolio as a solo venture capitalist requires a strategic approach to investment selection and portfolio management. Key steps include:
- Focus on Niche Markets: Specializing in specific industries or stages of startups can enhance expertise and deal flow.
- Diversify Investments: Spread investments across multiple startups to mitigate risk.
- Leverage Networks: Collaborate with other investors or join angel groups to access better opportunities.
What Skills Are Essential for a Solo Venture Capitalist?
To succeed as a solo venture capitalist, certain skills are indispensable. These include financial acumen, industry knowledge, and interpersonal abilities. Essential skills are:
- Financial Analysis: Ability to evaluate startup valuations, financial projections, and exit strategies.
- Negotiation Skills: Proficiency in structuring deals and negotiating terms with founders.
- Mentorship Abilities: Providing guidance and support to portfolio companies to drive their growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What educational background is typically required to become a venture capitalist?
To become a venture capitalist, a strong educational foundation is often essential. Many venture capitalists hold advanced degrees, such as an MBA from a top-tier business school, which provides them with the necessary skills in finance, strategy, and management. Additionally, degrees in fields like engineering, computer science, or life sciences can be advantageous, especially if you plan to focus on specific industries. However, while education is important, practical experience and a proven track record in entrepreneurship, investment banking, or private equity are often equally, if not more, critical.
What professional experience is necessary to enter the venture capital industry?
Professional experience is a key requirement for becoming a venture capitalist. Many successful venture capitalists have backgrounds in startups, investment banking, or management consulting, where they gained expertise in evaluating businesses and managing investments. Experience in entrepreneurship is particularly valuable, as it provides firsthand knowledge of the challenges startups face. Additionally, working in roles that involve financial analysis, deal structuring, or portfolio management can help build the skills needed to identify and support high-potential companies.
How important is networking in the venture capital field?
Networking is critical in the venture capital industry. Building strong relationships with entrepreneurs, investors, and other industry professionals can open doors to lucrative investment opportunities and partnerships. Many venture capitalists rely on their networks to source deals, conduct due diligence, and provide value to portfolio companies. Attending industry events, joining professional organizations, and leveraging platforms like LinkedIn can help you establish and grow your network. A robust network not only enhances your ability to find promising startups but also strengthens your reputation within the venture capital community.
What financial resources are needed to become a venture capitalist?
Becoming a venture capitalist often requires access to significant financial resources. While some venture capitalists use their own capital to invest, many raise funds from limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, family offices, or high-net-worth individuals. To attract LPs, you typically need a strong track record of successful investments or a compelling investment thesis. Additionally, having personal wealth or connections to wealthy individuals can help you secure the initial capital needed to start a venture capital fund. It's also important to have a deep understanding of financial modeling, valuation techniques, and risk management to make informed investment decisions.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles