Should I Quit Venture Capital to Join Real Estate Private Equity =37253896

Deciding whether to leave venture capital (VC) for real estate private equity (REPE) is a significant career crossroads that requires careful consideration. Both fields offer unique opportunities, challenges, and rewards, but they cater to different skill sets, risk appetites, and long-term goals. Venture capital thrives on innovation, high-risk investments in startups, and the potential for outsized returns, while real estate private equity focuses on tangible assets, stable cash flows, and value creation through property development or management. This article explores the key factors to weigh when contemplating such a transition, including industry dynamics, personal interests, financial implications, and career growth prospects.
-
Should I Quit Venture Capital to Join Real Estate Private Equity?
- What Are the Key Differences Between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Transitioning from VC to REPE?
- How Does the Skill Set Required for REPE Compare to VC?
- What Are the Financial Implications of Switching Careers?
- How Do Career Growth Opportunities Compare Between VC and REPE?
-
Can you go from venture capital to private equity?
- What is the Difference Between Venture Capital and Private Equity?
- Can Venture Capital Experience Help in Transitioning to Private Equity?
- What Skills Are Transferable from Venture Capital to Private Equity?
- What Challenges Might You Face When Moving from VC to PE?
- How Can You Prepare for a Transition from Venture Capital to Private Equity?
- Should I work in private equity or venture capital?
- Is real estate private equity worth it?
-
Why do people hate venture capitalists?
- Why do people perceive venture capitalists as greedy?
- How do venture capitalists contribute to income inequality?
- Why do people believe venture capitalists disrupt company culture?
- How do venture capitalists impact innovation negatively?
- Why are venture capitalists seen as out of touch with societal needs?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the key differences between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
- What factors should I consider before leaving Venture Capital for Real Estate Private Equity?
- How does the work culture differ between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
- What are the potential career growth opportunities in Real Estate Private Equity compared to Venture Capital?
Should I Quit Venture Capital to Join Real Estate Private Equity?
What Are the Key Differences Between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
Venture Capital (VC) and Real Estate Private Equity (REPE) are both investment strategies, but they differ significantly in their focus and approach. Venture Capital primarily invests in early-stage or high-growth companies, often in the technology or innovation sectors, with the goal of achieving high returns through equity stakes. On the other hand, Real Estate Private Equity focuses on acquiring, developing, or managing real estate assets, such as commercial properties, residential complexes, or land. The risk profiles, investment horizons, and required skill sets also vary between the two fields. VC is typically higher risk with potentially higher rewards, while REPE offers more stable, tangible assets with predictable cash flows.
See Also What Are the Key Differences Between Private Equity and Venture Capital
What Are the Key Differences Between Private Equity and Venture CapitalWhat Are the Pros and Cons of Transitioning from VC to REPE?
Transitioning from Venture Capital to Real Estate Private Equity has its advantages and disadvantages. Pros include the opportunity to work with tangible assets, which can provide more predictable returns and lower volatility compared to VC. REPE also often involves longer-term investments, which can be less stressful than the fast-paced, high-pressure environment of VC. Cons include the potential for lower returns compared to successful VC investments and the need to develop new expertise in real estate markets, property management, and regulatory frameworks. Additionally, the culture and networking opportunities in REPE may differ significantly from those in VC.
How Does the Skill Set Required for REPE Compare to VC?
The skill sets required for Real Estate Private Equity and Venture Capital overlap in areas like financial analysis, deal structuring, and negotiation. However, REPE demands a deeper understanding of real estate markets, property valuation, and asset management. In contrast, VC requires expertise in technology trends, startup ecosystems, and scaling businesses. Transitioning to REPE may require additional training or experience in real estate-specific areas, such as zoning laws, construction, and property development. Strong interpersonal skills are essential in both fields, but the nature of the relationships—with entrepreneurs in VC versus property developers and managers in REPE—can differ.
See Also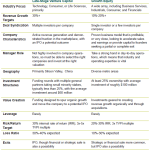 Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture Capital
Whats the Difference Between Growth Equity and Venture CapitalWhat Are the Financial Implications of Switching Careers?
Switching from Venture Capital to Real Estate Private Equity can have significant financial implications. While VC can offer substantial returns through equity stakes in successful startups, these returns are often uncertain and may take years to materialize. REPE, on the other hand, typically provides more stable income through management fees and predictable cash flows from real estate assets. However, the potential for outsized returns in REPE is generally lower than in VC. It's important to consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the current state of both markets before making a decision.
How Do Career Growth Opportunities Compare Between VC and REPE?
Career growth opportunities in Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity can vary based on your interests and long-term goals. In VC, career progression often involves moving from an analyst or associate role to a partner position, where you can influence investment decisions and build a portfolio of startups. In REPE, career growth may involve advancing from an analyst to a senior role in asset management or fund management, with opportunities to specialize in specific types of real estate investments. Both fields offer the potential for leadership roles, but the paths to achieving them differ significantly.
See Also Whats the Difference Between Venture Capital and Corporate Development
Whats the Difference Between Venture Capital and Corporate Development| Aspect | Venture Capital | Real Estate Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Startups and high-growth companies | Real estate assets and property development |
| Risk Profile | High risk, high reward | Lower risk, stable returns |
| Investment Horizon | Short to medium term | Long term |
| Skill Set | Technology trends, scaling businesses | Real estate markets, property management |
| Financial Returns | Potentially high but uncertain | Stable and predictable |
Can you go from venture capital to private equity?
What is the Difference Between Venture Capital and Private Equity?
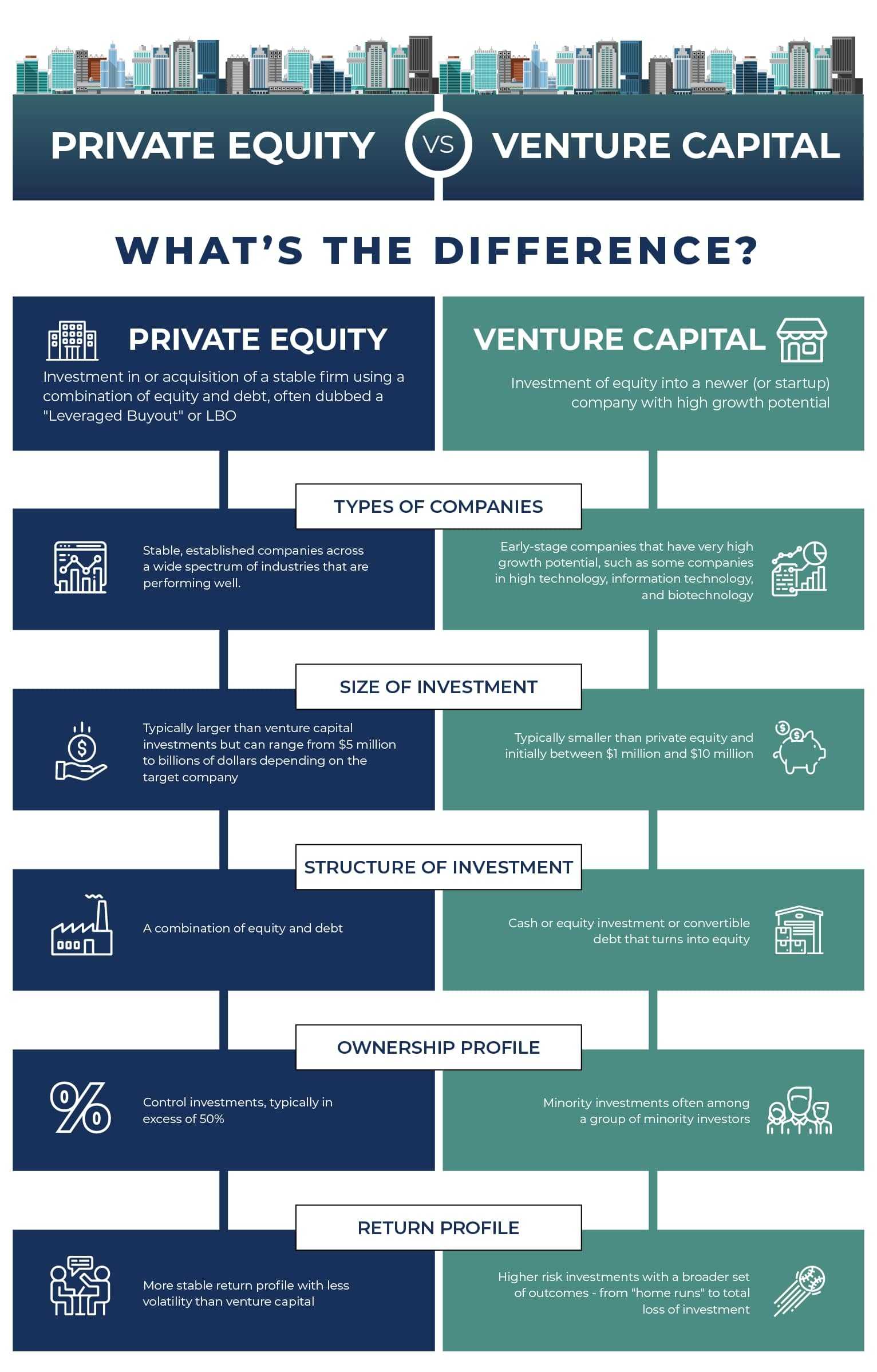
Venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) are both forms of investment, but they differ significantly in their focus and approach. Venture capital typically involves investing in early-stage or high-growth startups with high potential but also high risk. On the other hand, private equity focuses on more mature companies, often acquiring significant stakes or full ownership to drive operational improvements and growth. The key differences include:
See Also Whats the Difference Between a Venture Capitalist and an Entrepreneur
Whats the Difference Between a Venture Capitalist and an Entrepreneur- Stage of Investment: VC targets startups, while PE targets established companies.
- Risk Level: VC investments are riskier due to the early-stage nature of the companies.
- Investment Size: PE deals are generally larger in scale compared to VC investments.
Can Venture Capital Experience Help in Transitioning to Private Equity?
Yes, experience in venture capital can be beneficial when transitioning to private equity. Professionals in VC often develop skills that are transferable to PE, such as financial analysis, deal structuring, and portfolio management. However, there are some key areas where VC professionals may need to upskill:
- Deal Sourcing: PE often involves sourcing deals through networks and intermediaries, which may differ from VC's focus on startups.
- Operational Expertise: PE firms often require deeper operational knowledge to improve portfolio companies.
- Leveraged Buyouts: Understanding leveraged buyouts (LBOs) is crucial in PE, as they are a common investment strategy.
What Skills Are Transferable from Venture Capital to Private Equity?
Several skills acquired in venture capital are highly relevant in private equity. These include:
- Financial Modeling: Both VC and PE require strong financial modeling skills to evaluate investments.
- Due Diligence: Conducting thorough due diligence is critical in both fields to assess potential investments.
- Negotiation: Negotiating deal terms is a key skill in both VC and PE.
What Challenges Might You Face When Moving from VC to PE?
Transitioning from venture capital to private equity can present several challenges, including:
- Different Investment Horizons: PE investments typically have longer holding periods compared to VC.
- Operational Focus: PE often requires a hands-on approach to improve portfolio companies, which may be less common in VC.
- Deal Complexity: PE deals, especially leveraged buyouts, can be more complex than VC investments.
How Can You Prepare for a Transition from Venture Capital to Private Equity?
To successfully transition from venture capital to private equity, consider the following steps:
- Build Operational Expertise: Gain experience in operational roles or through additional training.
- Network with PE Professionals: Connect with individuals in the PE industry to understand their expectations and requirements.
- Learn About Leveraged Buyouts: Familiarize yourself with the mechanics and strategies of LBOs, as they are central to PE.
Should I work in private equity or venture capital?
What is the Difference Between Private Equity and Venture Capital?
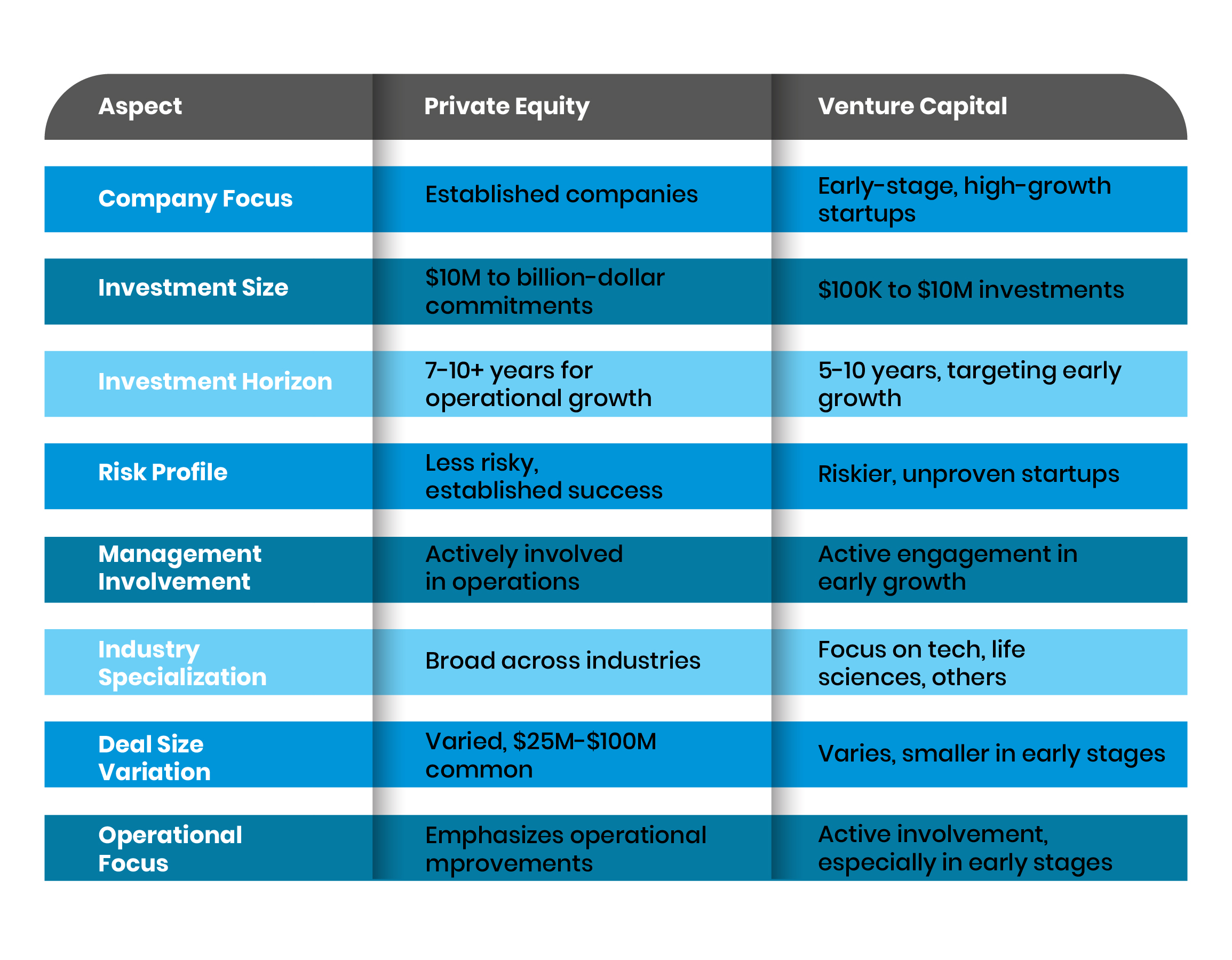
Private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) are both forms of investment, but they differ significantly in their focus and approach. Here are the key distinctions:
- Investment Stage: PE typically invests in mature companies, while VC focuses on early-stage or startup companies.
- Risk Level: VC investments are generally riskier due to the unproven nature of startups, whereas PE deals with established businesses.
- Capital Deployment: PE firms often use significant amounts of debt (leveraged buyouts), while VC firms rely on equity investments.
What Skills Are Required for Private Equity?
Working in private equity demands a specific skill set to succeed. Here are the most important skills:
- Financial Modeling: Proficiency in building and analyzing financial models is crucial for evaluating investments.
- Deal Structuring: Understanding how to structure deals, including debt and equity components, is essential.
- Negotiation: Strong negotiation skills are required to secure favorable terms for investments.
What Skills Are Required for Venture Capital?
Venture capital requires a unique combination of skills to identify and support high-potential startups. Key skills include:
- Market Analysis: Ability to assess market trends and identify emerging opportunities.
- Networking: Building relationships with entrepreneurs, investors, and industry experts is critical.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the potential of early-stage companies and their ability to scale.
What Are the Career Growth Opportunities in Private Equity?
Private equity offers a structured career path with significant growth potential. Here’s what you can expect:
- Analyst/Associate Roles: Entry-level positions focus on financial analysis and due diligence.
- Senior Roles: Progressing to roles like Vice President or Director involves managing deals and client relationships.
- Partner/Principal: At the top, you may become a partner, responsible for fund management and strategic decisions.
What Are the Career Growth Opportunities in Venture Capital?
Venture capital provides a dynamic career path with opportunities to work closely with innovative startups. Key stages include:
- Associate Roles: Entry-level positions involve sourcing deals and conducting due diligence.
- Principal Roles: Mid-level roles focus on leading investments and mentoring portfolio companies.
- Partner Roles: Senior positions involve fund management and strategic decision-making for the firm.
Is real estate private equity worth it?
What is Real Estate Private Equity?
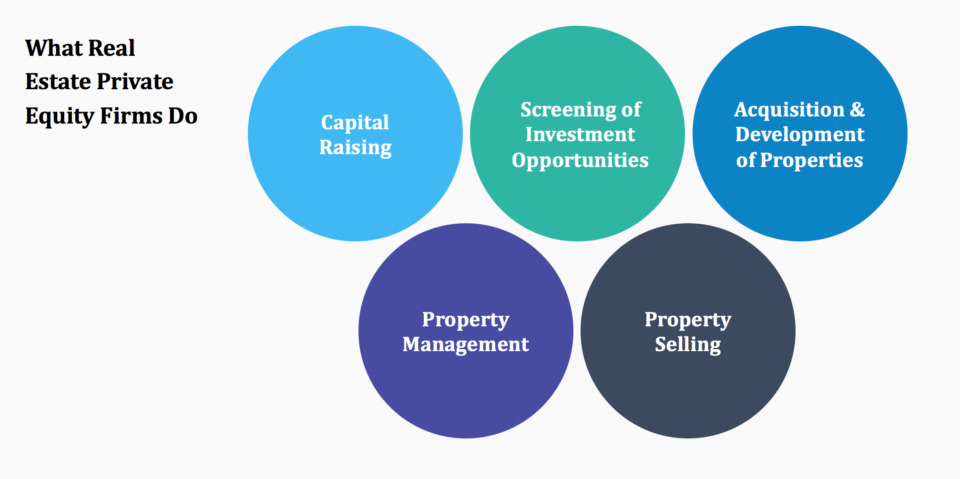
Real estate private equity (REPE) refers to a type of investment fund that pools capital from investors to acquire, develop, or manage real estate properties. These funds are typically managed by professional firms and aim to generate high returns through strategic property investments. REPE can include various property types, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or mixed-use developments. Investors in REPE funds are usually institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, or accredited investors seeking diversification and higher yields compared to traditional real estate investments.
- Pooled Capital: REPE funds aggregate money from multiple investors to make large-scale real estate investments.
- Professional Management: Experienced firms manage the funds, leveraging their expertise to maximize returns.
- Diverse Property Types: Investments can range from residential apartments to office buildings and industrial warehouses.
What Are the Benefits of Real Estate Private Equity?
Investing in real estate private equity offers several advantages, including the potential for high returns, diversification, and access to institutional-grade properties. REPE funds often target properties with significant upside potential, such as undervalued assets or development projects. Additionally, these investments can provide a hedge against inflation, as real estate values and rental incomes tend to rise with inflation. Investors also benefit from professional management, which reduces the need for direct involvement in property operations.
- High Returns: REPE funds aim for above-average returns through strategic investments.
- Diversification: Investors gain exposure to a variety of property types and markets.
- Inflation Hedge: Real estate often appreciates in value during inflationary periods.
What Are the Risks of Real Estate Private Equity?
While real estate private equity can be lucrative, it also carries significant risks. These include illiquidity, market volatility, and high fees. REPE investments are typically long-term, meaning investors may not be able to access their capital for several years. Additionally, real estate markets can be unpredictable, and economic downturns can negatively impact property values and rental incomes. Management and performance fees can also erode returns, making it essential to carefully evaluate the fund's structure and track record.
- Illiquidity: Capital is often locked up for extended periods, limiting access to funds.
- Market Volatility: Economic conditions can significantly affect property values and rental income.
- High Fees: Management and performance fees can reduce overall returns.
Who Should Invest in Real Estate Private Equity?
Real estate private equity is best suited for accredited investors or institutional investors with a high risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon. These investors typically have the financial capacity to withstand potential losses and the patience to wait for returns to materialize. REPE is also ideal for those seeking to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds. However, it may not be suitable for individuals who require liquidity or have a low risk tolerance.
- Accredited Investors: REPE is often restricted to individuals or entities meeting specific financial criteria.
- Long-Term Horizon: Investors should be prepared to commit capital for several years.
- Diversification Seekers: REPE offers exposure to alternative asset classes beyond traditional investments.
How Does Real Estate Private Equity Compare to Other Investments?
Compared to other investment options, real estate private equity offers unique advantages and challenges. Unlike publicly traded real estate investment trusts (REITs), REPE provides access to non-publicly traded properties and potentially higher returns. However, it also involves higher risks and less liquidity. Compared to direct real estate ownership, REPE allows investors to participate in large-scale projects without the need for hands-on management. However, it typically requires higher minimum investments and involves fees that direct ownership does not.
- Higher Returns: REPE often outperforms REITs and other traditional real estate investments.
- Less Liquidity: Unlike REITs, REPE investments are not easily tradable.
- Professional Management: REPE eliminates the need for direct property management, unlike direct ownership.
Why do people hate venture capitalists?

Why do people perceive venture capitalists as greedy?
Many people view venture capitalists as greedy due to their focus on maximizing returns on investments. This perception is fueled by several factors:
- High equity stakes: Venture capitalists often demand significant ownership in startups, which can lead to founders feeling exploited.
- Aggressive exit strategies: They prioritize quick exits, such as IPOs or acquisitions, which may not align with the long-term vision of the company.
- Profit-driven decisions: Their decisions are often driven by financial gains rather than the well-being of employees or the company's mission.
How do venture capitalists contribute to income inequality?
Venture capitalists are often criticized for exacerbating income inequality. This criticism stems from several key points:
- Wealth concentration: They tend to invest in high-growth startups, which primarily benefit already wealthy individuals and institutions.
- Limited access: Only a small group of entrepreneurs, often from privileged backgrounds, have access to venture capital funding.
- Disparity in returns: The profits from successful investments are disproportionately distributed, further widening the wealth gap.
Why do people believe venture capitalists disrupt company culture?
Venture capitalists are often blamed for disrupting company culture, particularly in startups. This belief is based on the following reasons:
- Pressure to scale: They push for rapid growth, which can lead to a loss of the original company values and culture.
- Focus on metrics: Their emphasis on performance metrics can create a high-pressure environment, eroding employee morale.
- Interference in management: They may influence hiring and operational decisions, leading to conflicts with the founding team.
How do venture capitalists impact innovation negatively?
While venture capitalists are often associated with fostering innovation, some argue they can have a negative impact. This perspective is supported by:
- Short-term focus: Their emphasis on quick returns can discourage long-term, groundbreaking innovation.
- Risk aversion: They may avoid funding truly innovative ideas that are considered too risky, favoring safer bets instead.
- Market saturation: They often fund similar startups, leading to market saturation and reduced diversity in innovation.
Why are venture capitalists seen as out of touch with societal needs?
Venture capitalists are sometimes criticized for being out of touch with broader societal needs. This criticism is rooted in:
- Elitist image: Their focus on high-tech and high-growth sectors can make them seem disconnected from everyday societal challenges.
- Lack of diversity: The venture capital industry is predominantly male and lacks diversity, which can lead to a narrow perspective on societal issues.
- Neglect of social impact: They often prioritize financial returns over social or environmental impact, leading to a perception of indifference to societal needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key differences between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
Venture Capital (VC) and Real Estate Private Equity (REPE) are distinct investment fields with different focuses. VC primarily invests in early-stage or growth-stage companies with high growth potential, often in technology or innovative sectors. It involves higher risk but also the possibility of significant returns if the startups succeed. On the other hand, REPE focuses on investing in real estate assets, such as commercial properties, residential developments, or infrastructure projects. The returns in REPE are typically more stable and predictable, driven by rental income, property appreciation, and strategic exits. Understanding these differences is crucial when deciding whether to transition from VC to REPE.
What factors should I consider before leaving Venture Capital for Real Estate Private Equity?
Before making the switch, consider factors such as your career goals, risk tolerance, and interest in the industries. If you enjoy working with startups and thrive in high-risk, high-reward environments, VC might be a better fit. However, if you prefer more stable, asset-backed investments and have an interest in real estate markets, REPE could be more appealing. Additionally, evaluate the skills required for each field. VC often demands expertise in technology, innovation, and scaling businesses, while REPE requires knowledge of property markets, financing structures, and asset management. Lastly, consider the long-term growth potential and compensation structures in both fields.
How does the work culture differ between Venture Capital and Real Estate Private Equity?
The work culture in Venture Capital is often fast-paced, dynamic, and entrepreneurial. Professionals in VC frequently interact with founders, attend pitch meetings, and analyze disruptive technologies. The environment is highly competitive, with a focus on identifying the next big thing. In contrast, Real Estate Private Equity tends to be more structured and methodical. The work involves analyzing property deals, managing portfolios, and working with developers or property managers. The pace may be slower compared to VC, but the focus on due diligence and long-term asset performance is critical. Understanding these cultural differences can help you determine which environment aligns better with your personality and work style.
What are the potential career growth opportunities in Real Estate Private Equity compared to Venture Capital?
Career growth in Real Estate Private Equity often involves progressing from analyst roles to senior positions such as asset manager, director, or partner. The industry offers opportunities to specialize in specific property types, such as residential, commercial, or industrial real estate. Additionally, REPE professionals can gain expertise in areas like debt financing, property development, and portfolio management. In Venture Capital, career growth typically involves moving from associate to principal or partner roles, with a focus on sourcing deals, managing investments, and supporting portfolio companies. Both fields offer lucrative career paths, but the choice depends on whether you prefer the stability of real estate or the excitement of working with startups and emerging technologies.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles