What Career is More Lucrative; Private Equity or Venture Capital?
The choice between a career in private equity (PE) or venture capital (VC) often hinges on factors such as financial rewards, job satisfaction, and long-term growth potential. Both fields are highly competitive and offer lucrative opportunities, but they differ significantly in their focus, risk profiles, and investment strategies. Private equity typically involves acquiring mature companies to optimize their operations and profitability, while venture capital focuses on funding early-stage startups with high growth potential. This article explores the key differences between these two career paths, examining salary prospects, skill requirements, and career trajectories to help aspiring professionals determine which path aligns best with their goals.
- What Career is More Lucrative: Private Equity or Venture Capital?
- Who makes more money, private equity or venture capital?
- Should I work in private equity or venture capital?
- Is private equity the most lucrative career?
- Is it harder to get into VC or PE?
-
Frequently Asked Questions by our Community
- What is the difference in earning potential between private equity and venture capital?
- Which career offers better long-term financial growth: private equity or venture capital?
- How do the career trajectories compare between private equity and venture capital?
- Which career is more suitable for someone interested in high-risk, high-reward investments?
What Career is More Lucrative: Private Equity or Venture Capital?
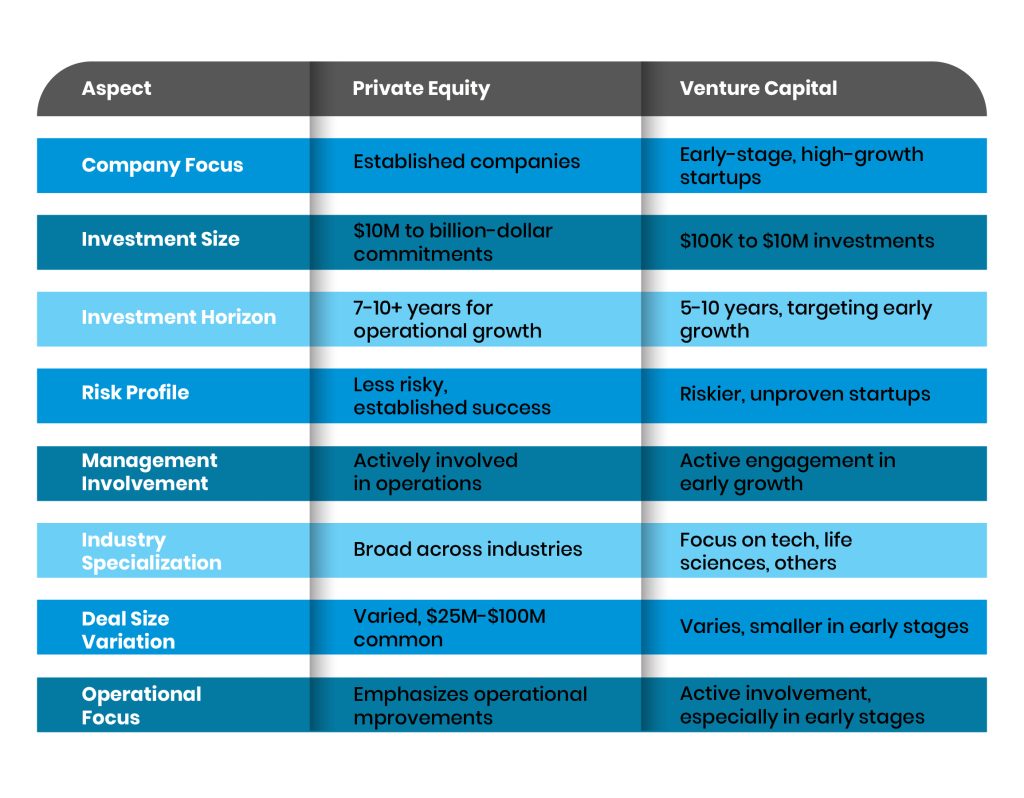
Understanding the Basics of Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private Equity (PE) and Venture Capital (VC) are both investment strategies, but they differ significantly in their approach and target companies. Private Equity typically involves investing in mature companies that are looking for capital to expand, restructure, or improve operations. These investments are often made through leveraged buyouts. On the other hand, Venture Capital focuses on early-stage companies with high growth potential, often in technology or innovative sectors. VC investments are riskier but can yield higher returns if the startup succeeds.
See AlsoWhat is the Average Irr Achieved by Venture Capital Funds?Salary and Compensation Comparison
When comparing salaries, Private Equity professionals generally earn higher base salaries compared to their Venture Capital counterparts. However, VC professionals often have the potential to earn significant bonuses and carried interest if their investments perform well. The table below provides a general comparison:
| Role | Average Base Salary | Average Bonus |
|---|---|---|
| Private Equity Associate | $120,000 - $150,000 | $50,000 - $100,000 |
| Venture Capital Associate | $100,000 - $130,000 | $30,000 - $80,000 |
Career Growth and Opportunities
Career growth in Private Equity often follows a more structured path, with clear progression from analyst to associate, vice president, and eventually partner. In Venture Capital, the path can be less linear, with opportunities to move into entrepreneurial roles or join portfolio companies. Both fields offer significant networking opportunities, but PE tends to have a more established hierarchy.
See Also Do Small Venture Funds 10m Also Follow the 2 20 Model or Do They Follow Other Models to Make the Economics Work at Small Fund Sizes
Do Small Venture Funds 10m Also Follow the 2 20 Model or Do They Follow Other Models to Make the Economics Work at Small Fund SizesRisk and Reward Profile
The risk and reward profiles of PE and VC are quite different. Private Equity investments are generally considered lower risk because they involve established companies with proven business models. However, the returns are often more predictable and steady. Venture Capital, on the other hand, involves higher risk due to the early-stage nature of the investments, but the potential rewards can be substantial if a startup becomes highly successful.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The future outlook for both Private Equity and Venture Capital is influenced by market trends and economic conditions. PE is seeing increased interest in sectors like healthcare and technology, while VC continues to thrive in innovation-driven industries such as artificial intelligence and biotechnology. Both fields are expected to grow, but the pace and nature of growth will differ based on market dynamics.
See Also How Do I Write a Good Cover Letter for a Internship at a Venture Capital Firm
How Do I Write a Good Cover Letter for a Internship at a Venture Capital FirmSkills and Qualifications Required
Both Private Equity and Venture Capital require strong analytical skills, financial acumen, and the ability to evaluate business models. However, PE professionals often need deeper expertise in financial modeling and due diligence, while VC professionals benefit from a keen understanding of emerging technologies and market trends. Networking and relationship-building skills are crucial in both fields, but VC may place a higher emphasis on identifying and nurturing entrepreneurial talent.
Who makes more money, private equity or venture capital?
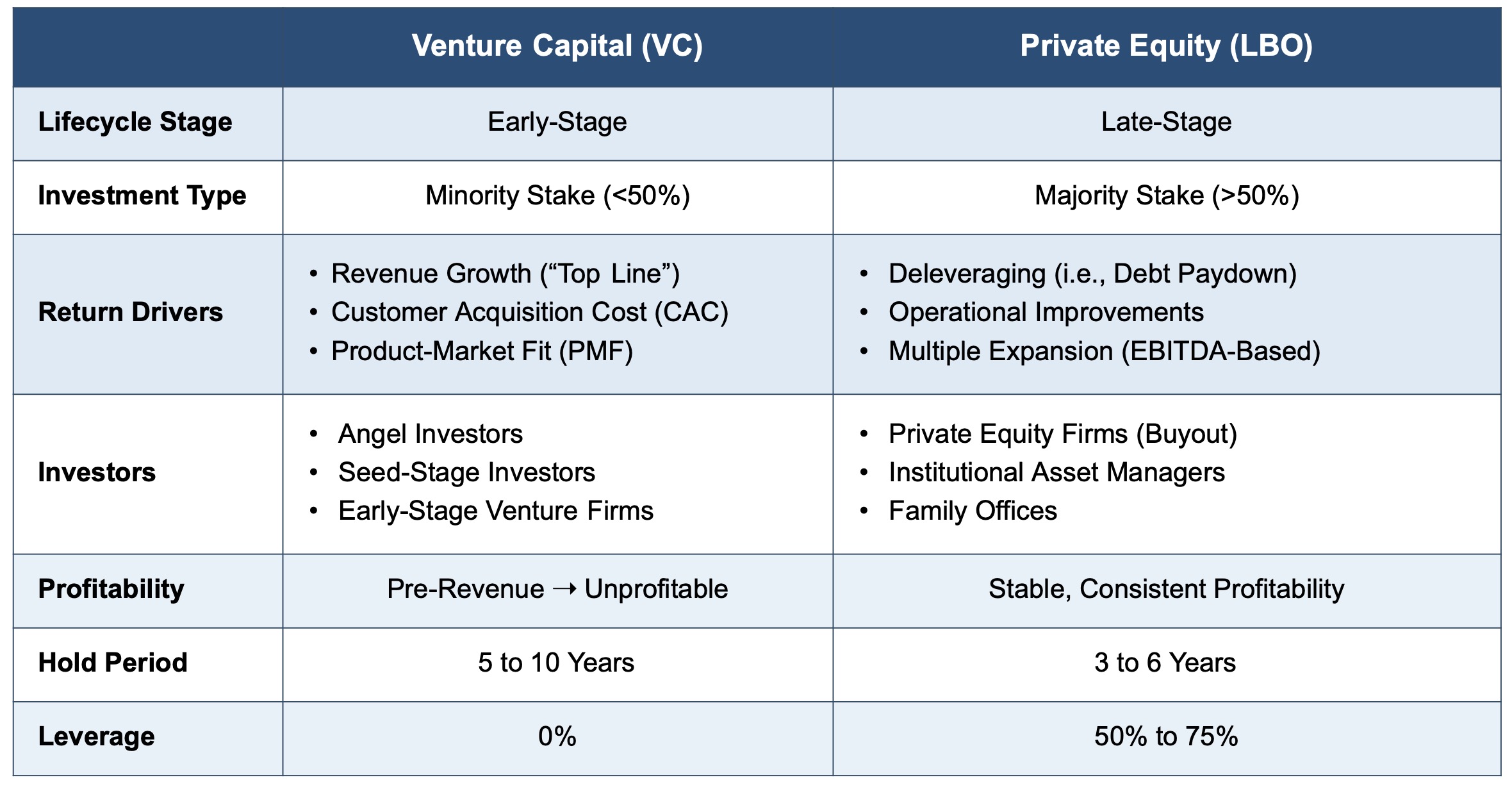
What is Private Equity?
Private equity (PE) involves investing in established companies, often taking a controlling stake, to improve operations and sell them later at a profit. PE firms typically target mature businesses with stable cash flows. Key aspects include:
- Leveraged buyouts (LBOs): PE firms use debt to acquire companies, aiming to increase their value over time.
- Long-term investments: PE investments usually last 4-7 years, focusing on operational improvements.
- High capital requirements: PE deals often involve large sums, limiting participation to institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals.
What is Venture Capital?
Venture capital (VC) focuses on early-stage or high-growth startups with significant potential but higher risk. VCs provide funding in exchange for equity and often take an active role in guiding the company. Key aspects include:
- High-risk, high-reward: VC investments target startups with exponential growth potential, though many fail.
- Early-stage focus: VCs often invest during seed or Series A rounds, when companies are still developing.
- Portfolio diversification: VCs spread investments across multiple startups to mitigate risk.
Earnings Potential in Private Equity
Private equity professionals often earn substantial incomes due to the size and structure of deals. Key factors influencing earnings include:
- Management fees: PE firms charge 1.5-2% of assets under management annually.
- Carried interest: PE professionals typically earn 20% of profits from successful exits.
- Deal size: Larger deals generate higher fees and profits, boosting overall earnings.
Earnings Potential in Venture Capital
Venture capital earnings can vary widely due to the high-risk nature of investments. Key factors influencing earnings include:
- Management fees: VCs charge 2-2.5% of assets under management annually.
- Carried interest: VCs earn 20-30% of profits from successful exits, though fewer exits occur compared to PE.
- Exit multiples: Successful startups can generate returns of 10x or more, significantly boosting earnings.
Who Makes More Money: Private Equity or Venture Capital?
The earnings comparison between private equity and venture capital depends on several factors:
- Deal success rate: PE has a higher success rate due to investing in established companies, while VC relies on a few high-performing startups.
- Fee structures: Both PE and VC earn management fees and carried interest, but PE deals are larger, often resulting in higher absolute earnings.
- Risk tolerance: VC offers higher potential returns but with greater risk, while PE provides more stable, predictable earnings.
Should I work in private equity or venture capital?
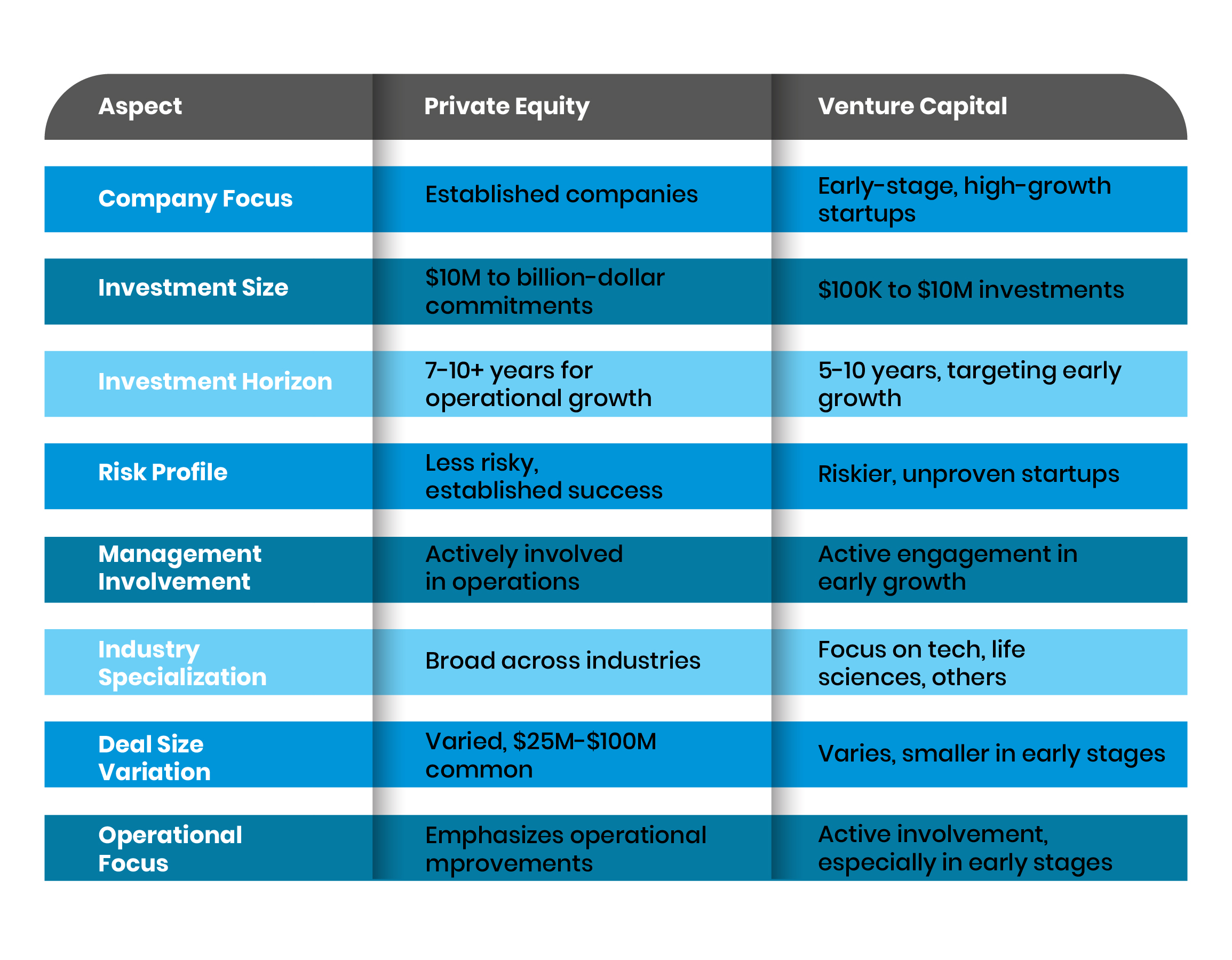
Understanding the Core Differences Between Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) are both investment strategies, but they differ significantly in their focus and approach. Here are the key distinctions:
- Investment Stage: PE typically invests in mature companies, while VC focuses on early-stage or startup companies.
- Risk and Return: VC investments are generally riskier but offer higher potential returns, whereas PE investments are more stable with moderate returns.
- Company Size: PE deals with larger, established firms, while VC targets smaller, high-growth potential startups.
Assessing Your Career Goals and Interests
Choosing between PE and VC depends on your career aspirations and personal interests. Consider the following:
- Industry Preference: If you are passionate about technology and innovation, VC might be more appealing. If you prefer working with established businesses, PE could be a better fit.
- Risk Tolerance: Are you comfortable with high-risk, high-reward scenarios? If so, VC might suit you. If you prefer stability, PE is likely more appropriate.
- Skill Set: VC often requires a strong understanding of emerging markets and technologies, while PE demands expertise in financial restructuring and operational improvements.
Evaluating the Work Environment and Culture
The work environment in PE and VC can vary significantly. Here’s what to expect:
- Work Hours: Both fields demand long hours, but VC might involve more unpredictability due to the nature of startups.
- Team Dynamics: VC firms are often smaller and more collaborative, while PE firms may have a more hierarchical structure.
- Deal Flow: VC professionals typically handle more deals simultaneously, whereas PE professionals focus on fewer, larger deals.
Considering Compensation and Career Growth
Compensation and career progression are crucial factors in your decision. Here’s a breakdown:
- Salary and Bonuses: Both fields offer competitive salaries, but PE often provides higher base salaries, while VC can offer significant bonuses based on successful exits.
- Career Advancement: PE may offer clearer career progression paths, whereas VC can provide quicker opportunities to take on significant responsibilities.
- Long-Term Earnings: Successful VC investments can yield substantial long-term earnings through equity stakes, whereas PE earnings are more tied to fund performance.
Analyzing Market Trends and Future Opportunities
Understanding market trends can help you make an informed decision. Consider these points:
- Market Growth: VC is booming in sectors like tech and biotech, while PE continues to thrive in traditional industries.
- Economic Cycles: PE is generally more resilient during economic downturns, whereas VC can be more volatile.
- Geographic Opportunities: Certain regions may offer more opportunities in VC or PE, depending on the local business ecosystem.
Is private equity the most lucrative career?

What Makes Private Equity a Lucrative Career?
Private equity is often considered one of the most lucrative careers due to its high earning potential and the nature of the work. Professionals in this field typically earn substantial salaries, bonuses, and carried interest, which can significantly increase their total compensation. The following factors contribute to its lucrative nature:
- High Compensation: Private equity professionals often earn six-figure salaries, with bonuses and profit-sharing adding to their income.
- Carried Interest: This is a share of the profits earned from investments, which can be a significant portion of total earnings.
- Deal-Driven Bonuses: Successful deals can lead to substantial bonuses, rewarding those who contribute to profitable outcomes.
What Are the Key Skills Required in Private Equity?
Success in private equity requires a unique set of skills that combine financial acumen, strategic thinking, and interpersonal abilities. These skills are essential for identifying lucrative investment opportunities and managing them effectively:
- Financial Analysis: Proficiency in analyzing financial statements and valuing companies is crucial.
- Negotiation Skills: Strong negotiation abilities are needed to secure favorable terms in deals.
- Strategic Thinking: The ability to develop and execute long-term investment strategies is key.
How Does Private Equity Compare to Other Finance Careers?
Private equity is often compared to other finance careers like investment banking, hedge funds, and venture capital. Each has its own set of advantages and challenges:
- Investment Banking: While investment banking offers high salaries, private equity often provides more significant long-term earning potential through carried interest.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds can offer high returns, but they also come with higher risk and volatility compared to private equity.
- Venture Capital: Venture capital focuses on early-stage companies, which can be riskier but also offer high rewards if successful.
What Are the Challenges of a Career in Private Equity?
Despite its lucrative nature, a career in private equity comes with its own set of challenges that can impact work-life balance and job satisfaction:
- Long Hours: The workload can be intense, with long hours required to close deals and manage investments.
- High Pressure: The stakes are high, and the pressure to deliver results can be stressful.
- Competitive Environment: The field is highly competitive, with a limited number of top-tier positions available.
What Are the Career Progression Opportunities in Private Equity?
Career progression in private equity can be highly rewarding, but it requires dedication and a proven track record of success:
- Analyst to Associate: Starting as an analyst, professionals can move up to associate roles with increased responsibilities.
- Vice President to Partner: With experience, one can advance to vice president and eventually partner, where they have a share in the firm's profits.
- Entrepreneurial Opportunities: Successful private equity professionals may start their own firms, leveraging their experience and network.
Is it harder to get into VC or PE?

What Are the Key Differences Between VC and PE?
Venture Capital (VC) and Private Equity (PE) are both investment fields, but they differ significantly in their focus and approach. VC typically involves investing in early-stage startups with high growth potential, while PE focuses on mature companies that require restructuring or growth capital. The entry barriers for each field vary based on these differences.
- VC firms often seek candidates with a strong background in entrepreneurship, technology, or innovation.
- PE firms prioritize candidates with experience in finance, consulting, or investment banking.
- The risk tolerance in VC is higher due to the nature of investing in unproven startups.
What Skills Are Required for VC and PE Roles?
Both VC and PE require a unique set of skills, but the emphasis varies. In VC, analytical thinking and networking are crucial for identifying promising startups. In PE, financial modeling and deal structuring are essential for evaluating and executing investments.
- VC roles demand a deep understanding of emerging markets and technologies.
- PE roles require expertise in financial analysis and operational improvement.
- Both fields value strong communication and negotiation skills.
How Competitive Are VC and PE Job Markets?
The job markets for both VC and PE are highly competitive, but the level of competition varies. VC roles are often harder to secure due to the limited number of positions and the niche expertise required. PE roles, while also competitive, are more structured and have a clearer career progression path.
- VC firms typically have smaller teams, leading to fewer job openings.
- PE firms often recruit from top-tier MBA programs and investment banks.
- Networking and personal connections play a significant role in securing VC roles.
What Are the Educational and Professional Backgrounds Needed?
Educational and professional backgrounds differ for VC and PE roles. VC firms often look for candidates with technical expertise or entrepreneurial experience, while PE firms prefer candidates with a strong foundation in finance and business.
- VC candidates may come from engineering, product management, or startup backgrounds.
- PE candidates often have experience in investment banking, consulting, or corporate finance.
- Advanced degrees like an MBA are more common in PE than in VC.
What Are the Career Progression Paths in VC and PE?
Career progression in VC and PE follows different trajectories. In VC, the path is less linear and often involves building a reputation through successful investments. In PE, the career ladder is more defined, with clear steps from analyst to partner.
- VC professionals may transition to founding startups or joining accelerators.
- PE professionals often move into senior management roles or start their own funds.
- Both fields offer opportunities for high financial rewards and professional growth.
Frequently Asked Questions by our Community
What is the difference in earning potential between private equity and venture capital?
The earning potential in both private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) can be substantial, but it often depends on the role, experience, and success of the investments. In private equity, professionals typically earn higher base salaries and bonuses due to the larger deal sizes and established nature of the companies they invest in. On the other hand, venture capital professionals may have lower base salaries but can earn significant returns through carried interest if their portfolio companies achieve high valuations or successful exits. Ultimately, the lucrative nature of each career depends on the individual's ability to generate returns and the stage of their career.
Which career offers better long-term financial growth: private equity or venture capital?
Both private equity and venture capital offer strong long-term financial growth opportunities, but the paths differ. In private equity, the focus is on acquiring mature companies, improving their operations, and selling them at a profit. This often leads to consistent and predictable returns over time. In contrast, venture capital involves investing in early-stage startups with high growth potential, which can result in exponential returns if the startups succeed. However, VC also carries higher risk, as many startups fail. For those seeking long-term financial growth, private equity may provide more stability, while venture capital offers the potential for outsized rewards.
How do the career trajectories compare between private equity and venture capital?
The career trajectories in private equity and venture capital can vary significantly. In private equity, professionals often start as analysts or associates, progressing to senior roles like vice president, principal, and eventually partner. The path is typically structured, with a focus on financial modeling, due diligence, and deal execution. In venture capital, the trajectory can be less linear, with many professionals entering the field after gaining experience in startups, entrepreneurship, or other industries. VC roles often emphasize networking, mentorship, and identifying disruptive technologies. Both careers offer lucrative opportunities, but private equity tends to have a more traditional and hierarchical progression.
Which career is more suitable for someone interested in high-risk, high-reward investments?
If you are drawn to high-risk, high-reward investments, venture capital may be the better fit. VC involves investing in early-stage companies with unproven business models, which can lead to significant losses if the startups fail. However, successful investments can yield extraordinary returns, especially if the startup goes public or is acquired. In contrast, private equity focuses on more established companies with proven cash flows, resulting in lower risk but also more modest returns. For those comfortable with uncertainty and excited by the potential of groundbreaking innovations, venture capital offers a more dynamic and potentially lucrative career path.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles