Are There Any Vcs Still Investing in Fabless Semiconductor Startups
The semiconductor industry has long been a cornerstone of technological innovation, with fabless semiconductor startups playing a pivotal role in driving advancements. These companies, which focus on design while outsourcing manufacturing, have historically attracted significant venture capital (VC) interest. However, as the industry matures and global supply chain challenges persist, questions arise about the current appetite of VCs for such investments. Are investors still willing to back fabless semiconductor startups, given the high capital requirements and long development cycles? This article explores the evolving landscape of VC funding in the fabless semiconductor sector, examining trends, challenges, and opportunities for emerging players in this competitive space.
- Are There Any VCs Still Investing in Fabless Semiconductor Startups?
- What kind of companies do VCs invest in?
- Which is the first fabless semiconductor company?
- Do VCs invest in Series C?
- Do VCs only invest in startups?
-
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Are venture capital firms still investing in fabless semiconductor startups?
- What factors make fabless semiconductor startups attractive to VCs?
- What challenges do fabless semiconductor startups face in securing VC funding?
- Which regions are seeing the most VC activity in fabless semiconductor startups?
Are There Any VCs Still Investing in Fabless Semiconductor Startups?
The semiconductor industry has always been a cornerstone of technological advancement, and fabless semiconductor startups play a crucial role in driving innovation. Despite the high costs and risks associated with this sector, several venture capital (VC) firms continue to invest in fabless semiconductor startups. These firms recognize the potential for significant returns, especially as demand for specialized chips grows in areas like artificial intelligence, IoT, and autonomous vehicles. Below, we explore the current landscape of VC investments in fabless semiconductor startups.
See AlsoWhy Are VCs Interested in Fabless Semiconductor Startups?
VCs are drawn to fabless semiconductor startups because of their ability to innovate without the burden of maintaining expensive fabrication facilities. These startups focus on design and intellectual property, which allows them to adapt quickly to market demands. Additionally, the increasing need for specialized chips in emerging technologies makes this sector highly attractive for investors seeking long-term growth.
What Challenges Do Fabless Semiconductor Startups Face?
Fabless semiconductor startups face several challenges, including high R&D costs, long development cycles, and intense competition. They also rely heavily on third-party manufacturers, which can lead to supply chain vulnerabilities. Despite these hurdles, successful startups can achieve significant market penetration and profitability, making them appealing to VCs willing to take calculated risks.
See Also Can Founders of a Failed Startup Be Sued Individually by Their Angel or Vc Investors
Can Founders of a Failed Startup Be Sued Individually by Their Angel or Vc InvestorsWhich VCs Are Actively Investing in This Sector?
Several prominent VCs have shown consistent interest in fabless semiconductor startups. Firms like Sequoia Capital, Andreessen Horowitz, and Intel Capital have made notable investments in this space. These firms often provide not only funding but also strategic guidance and industry connections to help startups scale effectively.
What Are the Key Trends Driving Investments?
The rise of AI, 5G, and edge computing has created a surge in demand for specialized semiconductors. VCs are particularly interested in startups that address these trends, as they represent the future of technology. Additionally, the global push for chip independence and supply chain resilience has further incentivized investments in this sector.
See Also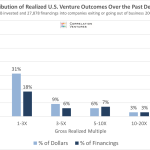 How Much in Returns Do Venture Capitalists Generally Expect for Their Investment in a Startup
How Much in Returns Do Venture Capitalists Generally Expect for Their Investment in a StartupHow Do Fabless Startups Compare to Traditional Semiconductor Companies?
Fabless startups differ from traditional semiconductor companies in that they do not own fabrication facilities. This model allows them to focus on innovation and reduce overhead costs. However, they must rely on partnerships with foundries, which can introduce risks. Despite this, the agility and specialization of fabless startups often give them a competitive edge in niche markets.
| VC Firm | Notable Investments | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Sequoia Capital | AI chips, IoT semiconductors | Emerging technologies |
| Andreessen Horowitz | 5G, edge computing chips | Next-gen connectivity |
| Intel Capital | Autonomous vehicle chips | Automotive innovation |
What kind of companies do VCs invest in?
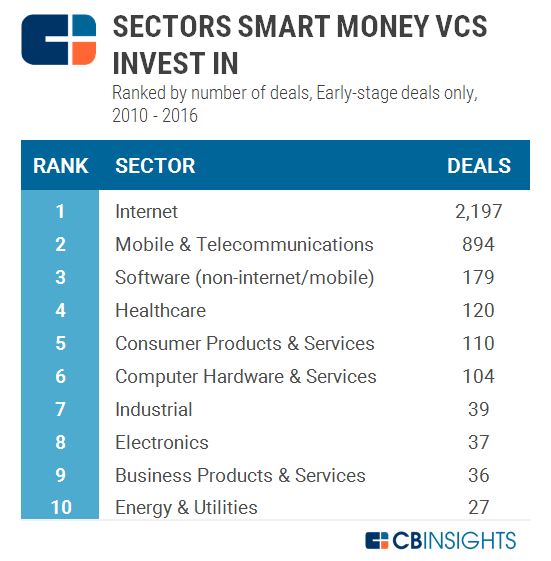
Early-Stage Startups with High Growth Potential
Venture capitalists (VCs) primarily invest in early-stage startups that demonstrate high growth potential. These companies are often in their seed or Series A funding stages and operate in industries like technology, biotech, or consumer goods. VCs look for businesses with scalable models, innovative solutions, and the ability to disrupt existing markets. Key factors include:
- Scalability: The ability to grow rapidly with minimal incremental costs.
- Innovation: Unique products or services that solve significant problems.
- Market Opportunity: A large or rapidly expanding target market.
Tech-Driven Companies
VCs are particularly drawn to tech-driven companies that leverage advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, blockchain, or software development. These firms often have the potential to revolutionize industries and create new markets. Key characteristics include:
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Proprietary technology or intellectual property.
- Digital Transformation: Solutions that enable businesses to transition to digital platforms.
- Global Reach: The ability to operate and scale across multiple regions.
Companies with Strong Founding Teams
A strong founding team is a critical factor for VCs when deciding to invest. They look for founders with a clear vision, industry expertise, and a track record of success. Key attributes include:
- Experience: Founders with prior entrepreneurial or industry experience.
- Leadership Skills: The ability to inspire and manage a growing team.
- Resilience: A demonstrated ability to overcome challenges and pivot when necessary.
Businesses with a Clear Path to Profitability
VCs invest in companies that have a clear path to profitability, even if they are not yet profitable at the time of investment. They evaluate the business model, revenue streams, and cost structure to ensure long-term sustainability. Key considerations include:
- Revenue Model: A well-defined and scalable revenue model.
- Unit Economics: Positive unit economics indicating profitability at scale.
- Market Traction: Evidence of customer demand and market validation.
Companies in Emerging or Underserved Markets
VCs often target companies operating in emerging or underserved markets where there is significant growth potential. These markets may lack competition or have unmet consumer needs. Key factors include:
- Market Gaps: Opportunities to address unmet needs or inefficiencies.
- First-Mover Advantage: The potential to establish a dominant position early.
- Regulatory Tailwinds: Favorable regulatory environments that support growth.
Which is the first fabless semiconductor company?
![]()
What is a Fabless Semiconductor Company?
A fabless semiconductor company is a business that designs and sells hardware and semiconductor chips but does not manufacture them in-house. Instead, these companies outsource the manufacturing process to specialized foundries. This model allows them to focus on innovation, design, and marketing while reducing the costs associated with building and maintaining fabrication facilities.
- Design Focus: Fabless companies prioritize research and development to create cutting-edge semiconductor designs.
- Cost Efficiency: Outsourcing manufacturing reduces capital expenditure and operational costs.
- Flexibility: They can adapt quickly to market demands without being tied to production facilities.
Who Founded the First Fabless Semiconductor Company?
The first fabless semiconductor company was LSI Logic, founded in 1981 by Wilfred Corrigan. Corrigan, a former executive at Fairchild Semiconductor, envisioned a business model that separated chip design from manufacturing, revolutionizing the semiconductor industry.
- Wilfred Corrigan: A pioneer in the semiconductor industry with extensive experience at Fairchild Semiconductor.
- Innovative Model: LSI Logic introduced the concept of fabless manufacturing, which became a standard in the industry.
- Legacy: Corrigan's vision paved the way for future fabless companies like Qualcomm and NVIDIA.
What Was the Impact of LSI Logic on the Semiconductor Industry?
LSI Logic had a profound impact on the semiconductor industry by demonstrating the viability of the fabless business model. This approach allowed companies to innovate faster and reduce costs, leading to a more dynamic and competitive market.
- Market Transformation: The fabless model enabled smaller companies to compete with established semiconductor giants.
- Increased Innovation: By focusing on design, companies could bring new technologies to market more quickly.
- Global Expansion: The model facilitated the growth of semiconductor industries in regions without fabrication facilities.
How Did the Fabless Model Evolve After LSI Logic?
After the success of LSI Logic, the fabless model gained widespread adoption. Companies like Qualcomm, Broadcom, and NVIDIA embraced this approach, leading to significant advancements in semiconductor technology and market growth.
- Qualcomm: Became a leader in wireless communication technologies using the fabless model.
- Broadcom: Specialized in broadband and networking solutions, leveraging fabless manufacturing.
- NVIDIA: Revolutionized graphics processing units (GPUs) through innovative design and outsourcing.
What Are the Key Advantages of the Fabless Semiconductor Model?
The fabless semiconductor model offers several advantages, including reduced costs, faster time-to-market, and the ability to focus on core competencies like design and innovation.
- Cost Reduction: Eliminates the need for expensive fabrication facilities.
- Faster Innovation: Companies can quickly adapt to technological advancements and market trends.
- Specialization: Allows firms to focus on design and development without the burden of manufacturing.
Do VCs invest in Series C?

What is Series C Funding?
Series C funding is a later-stage investment round where companies seek capital to scale operations, expand into new markets, or prepare for an IPO. At this stage, the company has typically demonstrated strong growth, a proven business model, and significant revenue. Investors in Series C rounds often include venture capital firms (VCs), private equity firms, and sometimes hedge funds.
- Purpose: Scaling operations, entering new markets, or preparing for an IPO.
- Investors: VCs, private equity firms, and hedge funds.
- Company Stage: Established companies with proven growth and revenue.
Do VCs Participate in Series C Rounds?
Yes, venture capital firms (VCs) do participate in Series C funding rounds, although their involvement may differ from earlier stages. At this stage, VCs often co-invest with other institutional investors, such as private equity firms or hedge funds, to provide the substantial capital required for scaling.
- Co-Investment: VCs often partner with other institutional investors.
- Capital Requirements: Series C rounds typically involve larger funding amounts.
- Risk Profile: Lower risk compared to earlier stages due to proven business models.
Why Do VCs Invest in Series C?
VCs invest in Series C rounds because these companies have already demonstrated market traction, scalability, and a clear path to profitability. The risk is lower compared to seed or Series A stages, and the potential for a high return on investment (ROI) remains significant, especially if the company goes public or is acquired.
- Market Traction: Proven customer base and revenue streams.
- Scalability: Clear potential for rapid growth.
- Exit Opportunities: High likelihood of IPO or acquisition.
What Types of VCs Invest in Series C?
In Series C rounds, late-stage VCs and growth equity firms are the most active. These investors specialize in providing capital to mature companies that are scaling rapidly. Additionally, some traditional early-stage VCs may participate if they have a prior relationship with the company.
- Late-Stage VCs: Focus on scaling and growth.
- Growth Equity Firms: Target companies with proven business models.
- Early-Stage VCs: May participate if they have existing ties to the company.
How Does Series C Differ from Earlier Funding Rounds?
Series C funding differs from earlier rounds like seed, Series A, or Series B in terms of investment size, investor profile, and company maturity. At this stage, companies are more established, and the focus shifts from product development to scaling and market dominance.
- Investment Size: Larger amounts compared to earlier rounds.
- Investor Profile: More institutional investors and fewer angel investors.
- Company Maturity: Established businesses with proven success.
Do VCs only invest in startups?
Do VCs Only Invest in Startups?
No, venture capitalists (VCs) do not only invest in startups. While startups are a primary focus due to their high growth potential, VCs also invest in other types of businesses, including established companies seeking expansion, innovative projects, or scaling opportunities. Their investment criteria often revolve around high-growth potential, scalability, and the ability to generate significant returns.
- Startups: VCs frequently invest in early-stage companies with innovative ideas and high growth potential.
- Growth-Stage Companies: VCs may fund companies that have already proven their business model and are looking to scale.
- Established Companies: Some VCs invest in mature companies undergoing significant transformations or expansions.
What Types of Companies Do VCs Typically Invest In?
VCs typically invest in companies that demonstrate high growth potential, scalability, and innovation. These can range from early-stage startups to more mature businesses. The key factor is the potential for significant returns on investment.
- Tech Startups: Companies in the technology sector are a favorite due to their rapid growth and scalability.
- Biotech and Healthcare: Innovative solutions in healthcare often attract VC funding.
- Consumer Goods: Companies with unique products or services that can scale quickly.
Why Do VCs Prefer Startups?
VCs prefer startups because they offer the potential for exponential growth and high returns. Startups often operate in emerging markets or introduce disruptive technologies, making them attractive investment opportunities.
- High Growth Potential: Startups can grow rapidly, offering significant returns.
- Innovation: Startups often bring new ideas and technologies to the market.
- Equity Stake: VCs can acquire a substantial equity stake in startups, increasing their potential returns.
Can VCs Invest in Non-Startup Businesses?
Yes, VCs can and do invest in non-startup businesses. These include established companies looking to expand, enter new markets, or innovate their product lines. The focus remains on high-growth potential and scalability.
- Expansion Funding: VCs may fund companies looking to expand into new regions or markets.
- Product Innovation: Established companies developing new products or services may attract VC investment.
- Turnaround Projects: VCs sometimes invest in companies undergoing significant transformations.
What Are the Risks for VCs Investing Outside Startups?
Investing outside startups carries different risks, such as market saturation, lower growth rates, and higher competition. However, these investments can still offer substantial returns if the company successfully executes its growth strategy.
- Market Saturation: Established markets may have limited growth potential.
- Competition: Mature markets often have more competitors, reducing profit margins.
- Execution Risk: The success of the investment depends heavily on the company's ability to execute its plans effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are venture capital firms still investing in fabless semiconductor startups?
Yes, venture capital firms are still investing in fabless semiconductor startups, although the landscape has become more selective. The semiconductor industry is highly competitive and capital-intensive, but the demand for innovative chip designs, especially in areas like AI, IoT, and automotive technologies, continues to attract investors. VCs are particularly interested in startups that offer unique solutions, scalability, and the potential to disrupt traditional markets.
What factors make fabless semiconductor startups attractive to VCs?
Fabless semiconductor startups are attractive to VCs due to their lower capital requirements compared to traditional semiconductor companies that own fabrication facilities. These startups focus on design and innovation, outsourcing manufacturing to third-party foundries. Additionally, the growing demand for specialized chips in sectors like 5G, edge computing, and renewable energy creates opportunities for startups to carve out niche markets, making them appealing to investors seeking high-growth potential.
What challenges do fabless semiconductor startups face in securing VC funding?
Fabless semiconductor startups face several challenges in securing VC funding, including the high cost of R&D, long development cycles, and intense competition from established players. Investors often scrutinize the startup's technical expertise, intellectual property portfolio, and market differentiation. Additionally, the cyclical nature of the semiconductor industry and geopolitical factors, such as supply chain disruptions, can make VCs more cautious when evaluating opportunities in this space.
Which regions are seeing the most VC activity in fabless semiconductor startups?
Regions like Silicon Valley in the U.S., China, and Europe are seeing significant VC activity in fabless semiconductor startups. Silicon Valley remains a hub for innovation and investment due to its strong ecosystem of tech companies and venture capital firms. China is also a major player, driven by government support and a focus on achieving semiconductor self-sufficiency. In Europe, countries like Germany and the Netherlands are emerging as key players, supported by initiatives to boost local semiconductor production and innovation.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles