What is a Venture Capitalists End Goal?

Venture capitalists (VCs) play a pivotal role in the growth of startups and innovative businesses, providing not only financial backing but also strategic guidance. However, their involvement goes beyond mere investment. The end goal of a venture capitalist is multifaceted, encompassing financial returns, portfolio diversification, and fostering innovation. While their primary objective is to achieve substantial returns on investment through successful exits, such as IPOs or acquisitions, VCs also aim to build long-term relationships with entrepreneurs and contribute to the development of groundbreaking technologies. Understanding the motivations and end goals of venture capitalists is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking funding and navigating the complex world of startup financing.
What is a Venture Capitalist's End Goal?
Venture capitalists (VCs) are investors who provide capital to startups and early-stage companies with high growth potential. Their primary objective is to achieve a significant return on investment (ROI) by supporting businesses that can scale rapidly and generate substantial profits. However, their end goal extends beyond just financial gains. VCs also aim to build a strong portfolio, establish industry influence, and foster innovation. Below, we explore the key aspects of a venture capitalist's end goal in detail.
See Also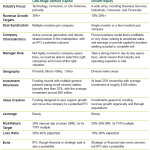 What is the Difference Between Early and Late Stage Venture Capital
What is the Difference Between Early and Late Stage Venture Capital1. Maximizing Return on Investment (ROI)
The ultimate goal of a venture capitalist is to maximize their return on investment. VCs invest in high-risk, high-reward startups with the expectation that a few successful exits (such as IPOs or acquisitions) will yield substantial profits. They typically aim for a 10x to 20x return on their initial investment to compensate for the high failure rate of startups.
2. Building a Strong Portfolio
A venture capitalist's success is often measured by the strength of their investment portfolio. By diversifying investments across multiple startups and industries, VCs mitigate risks and increase the likelihood of having unicorn companies (startups valued at over $1 billion) in their portfolio. A strong portfolio not only generates financial returns but also enhances the VC's reputation in the industry.
See Also What is Difference Between Angel Investor and Venture Capitalist
What is Difference Between Angel Investor and Venture Capitalist3. Establishing Industry Influence
Venture capitalists often seek to establish themselves as key players in specific industries. By investing in innovative startups and providing mentorship, VCs can shape the direction of emerging markets and technologies. This influence allows them to attract top talent, secure better deals, and gain access to exclusive investment opportunities.
4. Fostering Innovation and Disruption
VCs play a crucial role in fostering innovation and disruption by funding startups that challenge traditional business models. Their end goal includes supporting groundbreaking technologies and solutions that can transform industries, create new markets, and address global challenges. This aligns with their mission to drive long-term societal impact alongside financial success.
See Also I Work for a Vc Company That S Not Looking for Unicorns is There Any Chance They Can Succeed How Does This Even Make Sense
I Work for a Vc Company That S Not Looking for Unicorns is There Any Chance They Can Succeed How Does This Even Make Sense5. Achieving Successful Exits
A critical component of a venture capitalist's end goal is achieving successful exits for their investments. This typically involves guiding startups toward initial public offerings (IPOs) or facilitating acquisitions by larger companies. Successful exits not only provide financial returns but also validate the VC's ability to identify and nurture high-potential businesses.
| Key Objective | Description |
|---|---|
| Maximizing ROI | Achieving high returns through successful startup exits. |
| Building a Strong Portfolio | Diversifying investments to include high-growth startups. |
| Establishing Industry Influence | Becoming a key player in shaping emerging markets. |
| Fostering Innovation | Supporting disruptive technologies and business models. |
| Achieving Successful Exits | Guiding startups toward IPOs or acquisitions. |
What is the main goal of a venture capitalist?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/venture-capitalist-4187107-1-279ebe8e1bb9410a9f8c3cf7dc47c7cb.jpg)
The main goal of a venture capitalist is to invest in high-potential startups or early-stage companies with the aim of achieving significant financial returns. Venture capitalists provide capital, expertise, and resources to help these companies grow, with the expectation of exiting their investment through events like an IPO (Initial Public Offering) or acquisition at a much higher valuation.
What Drives Venture Capitalists to Invest?
Venture capitalists are driven by the potential for high returns on investment. They focus on companies with innovative ideas, scalable business models, and strong growth potential. Key factors include:
- Market opportunity: The size and growth potential of the target market.
- Team quality: The expertise and track record of the founding team.
- Innovation: The uniqueness and defensibility of the product or service.
How Do Venture Capitalists Evaluate Startups?
Venture capitalists use a rigorous evaluation process to identify promising startups. This involves:
- Due diligence: Analyzing financials, market position, and competitive landscape.
- Scalability: Assessing whether the business can grow rapidly with minimal incremental costs.
- Exit potential: Evaluating the likelihood of a successful exit through IPO or acquisition.
What Role Do Venture Capitalists Play in a Startup's Growth?
Beyond funding, venture capitalists provide strategic guidance and mentorship to startups. Their roles include:
- Networking: Connecting startups with industry experts, partners, and customers.
- Operational support: Assisting with hiring, scaling operations, and refining business strategies.
- Risk management: Helping startups navigate challenges and mitigate risks.
What Are the Risks Associated with Venture Capital Investments?
Venture capital investments are inherently risky due to the high failure rate of startups. Key risks include:
- Market risk: Changes in market demand or competitive dynamics.
- Execution risk: The startup's ability to deliver on its business plan.
- Liquidity risk: Difficulty in exiting the investment due to lack of buyers or market conditions.
How Do Venture Capitalists Achieve Returns on Their Investments?
Venture capitalists aim to achieve returns through capital appreciation and exit strategies. Common methods include:
- IPOs: Taking the company public to sell shares at a higher valuation.
- Acquisitions: Selling the company to a larger firm for a premium.
- Secondary sales: Selling their equity stake to other investors or private equity firms.
What is the last stage of venture capital?
Understanding the Last Stage of Venture Capital
The last stage of venture capital, often referred to as the late-stage funding, is the phase where a startup has already demonstrated significant growth, market traction, and revenue generation. At this point, the company is typically preparing for an exit strategy, such as an initial public offering (IPO) or acquisition. Investors in this stage are usually focused on scaling the business further and maximizing returns before the exit.
- Late-stage funding is aimed at companies with proven business models.
- Investors focus on scaling operations and preparing for an exit.
- This stage often involves larger funding rounds compared to earlier stages.
Key Characteristics of Late-Stage Venture Capital
Late-stage venture capital is characterized by several distinct features. Companies at this stage have typically achieved product-market fit, have a strong customer base, and are generating consistent revenue. The funding rounds are often led by private equity firms, hedge funds, or sovereign wealth funds, rather than traditional venture capital firms.
- Companies have a proven track record of growth and profitability.
- Investors are more focused on financial metrics and less on potential.
- Funding amounts are significantly higher, often in the hundreds of millions.
Types of Investors in Late-Stage Venture Capital
In the late-stage venture capital phase, the investor landscape changes significantly. Traditional venture capital firms may still participate, but they are often joined by institutional investors, private equity firms, and even corporate investors. These investors bring not only capital but also strategic resources to help the company scale rapidly.
- Private equity firms often lead late-stage funding rounds.
- Institutional investors like pension funds and endowments participate.
- Corporate investors may seek strategic partnerships or acquisitions.
Purpose of Late-Stage Venture Capital Funding
The primary purpose of late-stage venture capital funding is to accelerate growth and prepare the company for a successful exit. This could involve expanding into new markets, increasing production capacity, or enhancing the product line. The goal is to maximize the company's valuation before it goes public or is acquired.
- Funding is used to scale operations and enter new markets.
- Companies may invest in research and development to enhance their offerings.
- Preparing for an IPO or acquisition is a key focus.
Risks and Challenges in Late-Stage Venture Capital
While late-stage venture capital offers significant opportunities, it also comes with its own set of risks and challenges. The high valuation of companies at this stage means that investors are paying a premium, which can lead to lower returns if the exit does not meet expectations. Additionally, the pressure to scale quickly can sometimes lead to operational inefficiencies or overexpansion.
- High valuations can result in lower returns for investors.
- Rapid scaling may lead to operational challenges.
- Market conditions can impact the success of an IPO or acquisition.
What is the exit value in VC?

What is Exit Value in Venture Capital?
The exit value in venture capital refers to the amount of money a startup or company is sold for during an exit event, such as an acquisition, merger, or initial public offering (IPO). This value determines the return on investment (ROI) for venture capitalists (VCs) and other stakeholders. It is a critical metric because it directly impacts the profitability of the investment and influences future funding decisions.
- Exit value is calculated based on the sale price of the company or its shares.
- It includes the total proceeds from the exit event, minus any outstanding debts or liabilities.
- The exit value is often compared to the initial investment to determine the success of the venture.
Why is Exit Value Important in Venture Capital?
The exit value is crucial in venture capital because it determines the financial success of an investment. VCs rely on high exit values to generate significant returns, which are then reinvested into new startups. A strong exit value also enhances the reputation of the VC firm, attracting more investors and high-quality startups.
- It provides a clear measure of the investment's performance.
- High exit values attract more investors to the VC firm.
- It influences the firm's ability to raise future funds.
How is Exit Value Calculated?
Calculating the exit value involves assessing the total proceeds from the exit event. This includes the sale price of the company, any additional payments, and the value of retained equity. The calculation also considers factors like market conditions, company performance, and negotiation outcomes.
- Determine the total sale price of the company or its shares.
- Subtract any outstanding debts, liabilities, or transaction costs.
- Include the value of any retained equity or earn-outs.
Types of Exit Events in Venture Capital
There are several types of exit events that can determine the exit value in venture capital. These include acquisitions, mergers, IPOs, and secondary sales. Each type of exit event has its own implications for the exit value and the stakeholders involved.
- Acquisitions: The company is purchased by another entity, often at a premium.
- Mergers: The company combines with another, creating a new entity with shared ownership.
- IPOs: The company goes public, allowing shares to be traded on the stock market.
Factors Influencing Exit Value
Several factors can influence the exit value in venture capital, including market conditions, company performance, and investor demand. A strong market, high growth potential, and competitive bidding can drive up the exit value, while poor performance or unfavorable conditions can reduce it.
- Market conditions: A bullish market can increase exit values.
- Company performance: Strong revenue growth and profitability boost exit values.
- Investor demand: High interest from buyers or investors can drive up the price.
What do venture capitalists want in return?

Equity Stake in the Company
Venture capitalists typically seek an equity stake in the companies they invest in. This means they acquire a percentage of ownership in the business. In return for their investment, they expect to benefit from the company's growth and eventual success. The equity stake allows them to:
- Share in the profits when the company generates revenue or is sold.
- Influence decision-making by having a say in major business decisions.
- Exit with significant returns through an IPO, acquisition, or merger.
High Return on Investment (ROI)
Venture capitalists are primarily motivated by the potential for a high return on investment. They invest in high-risk, high-reward startups and expect substantial financial gains. To achieve this, they focus on:
- Scalable business models that can grow rapidly and generate significant revenue.
- Innovative products or services with a competitive edge in the market.
- Strong management teams capable of executing the business plan effectively.
Board Seats and Influence
Venture capitalists often request board seats as part of their investment terms. This allows them to actively participate in the company's strategic direction. Their involvement includes:
- Providing guidance and mentorship to the founding team.
- Monitoring progress to ensure the company meets its milestones.
- Protecting their investment by having a direct role in key decisions.
Exit Strategy
A clear exit strategy is crucial for venture capitalists. They invest with the intention of eventually exiting the investment to realize their returns. Common exit strategies include:
- Initial Public Offering (IPO), where the company goes public and shares are sold on the stock market.
- Acquisition or merger, where the company is sold to another business.
- Secondary market sales, where their equity stake is sold to other investors.
Milestones and Performance Metrics
Venture capitalists often set milestones and performance metrics to track the company's progress. These benchmarks ensure that the business is on track to achieve its goals. Key aspects include:
- Revenue targets to measure financial growth.
- Customer acquisition rates to assess market penetration.
- Product development timelines to ensure innovation and competitiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary objective of a venture capitalist?
The primary objective of a venture capitalist is to generate substantial returns on their investments. Venture capitalists invest in early-stage or high-growth companies with the expectation that these companies will grow significantly and provide a profitable exit strategy, such as an IPO (Initial Public Offering) or an acquisition. Their ultimate goal is to maximize the value of their investment portfolio while managing risk.
How do venture capitalists measure success?
Venture capitalists measure success primarily through financial returns. They evaluate the performance of their investments based on metrics such as Internal Rate of Return (IRR), cash-on-cash returns, and the overall growth of the portfolio. Additionally, they consider the strategic impact of their investments, such as fostering innovation or creating market-leading companies, as part of their broader success criteria.
What role does exit strategy play in a venture capitalist's end goal?
An exit strategy is critical to a venture capitalist's end goal because it determines how they will realize returns on their investments. Common exit strategies include selling the company to a larger corporation, taking the company public through an IPO, or facilitating a merger. The chosen exit strategy must align with the growth trajectory of the company and provide the highest possible return on investment.
Do venture capitalists focus solely on financial gains?
While financial gains are the primary focus, venture capitalists also consider other factors such as industry impact, innovation, and long-term value creation. Many venture capitalists aim to support companies that can disrupt industries, create jobs, and contribute to economic growth. However, these non-financial goals are often secondary to achieving strong financial returns for their investors.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles