What is the Worst Part of Being a Vc?
Venture capital (VC) is often glamorized as a high-stakes, high-reward career, offering the thrill of funding groundbreaking startups and reaping substantial returns. However, beneath the surface lies a world of challenges that can make the role far from ideal. From the constant pressure to identify the next unicorn to the emotional toll of frequent failures, being a VC is not for the faint of heart. The worst part of the job often revolves around the inherent uncertainty and the weight of decision-making, where one wrong bet can lead to significant losses. This article delves into the less-discussed struggles that define the VC experience.
What is the Worst Part of Being a VC?
Being a Venture Capitalist (VC) can be an exciting and rewarding career, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. The worst part of being a VC often revolves around the high-pressure environment, uncertainty, and the emotional toll of dealing with startups that may fail despite significant investments. Below, we explore the key aspects that make this role particularly demanding.
See Also What is the Typical Structure of a Vc Fund?
What is the Typical Structure of a Vc Fund?The Emotional Toll of Startup Failures
One of the most challenging aspects of being a VC is dealing with the emotional impact of startup failures. Despite thorough due diligence, many startups fail, and watching a company you’ve invested in collapse can be heartbreaking. VCs often form close relationships with founders, making it even harder to detach emotionally when things go south.
High Pressure to Deliver Returns
VCs operate in a high-stakes environment where the pressure to deliver significant returns to investors is immense. Limited Partners (LPs) expect high returns on their investments, and failing to meet these expectations can damage a VC’s reputation and future fundraising efforts. This constant pressure can lead to stress and burnout.
See Also What is Difference Between Angel Investor and Venture Capitalist
What is Difference Between Angel Investor and Venture CapitalistDealing with Uncertainty
The uncertainty inherent in the startup world is another major challenge. Even with the best research and analysis, predicting which startups will succeed is incredibly difficult. This unpredictability can make decision-making stressful and risky, as VCs must often rely on intuition and experience rather than concrete data.
Long Investment Horizons
VC investments typically have long horizons, often taking 7-10 years to mature. This means that VCs must be patient and prepared to wait for extended periods before seeing any returns. During this time, they must continue to manage their portfolios, support their startups, and navigate the ever-changing market landscape.
See AlsoHow Do Venture Capitalists Actually Work?Intense Competition
The VC industry is highly competitive, with many investors vying for the same promising startups. This competition can drive up valuations, making it harder to secure deals at reasonable prices. Additionally, VCs must constantly network and build relationships to stay ahead, which can be time-consuming and exhausting.
| Aspect | Challenge |
|---|---|
| Emotional Toll | Dealing with startup failures and emotional attachment |
| High Pressure | Delivering returns to investors |
| Uncertainty | Predicting startup success |
| Long Horizons | Waiting 7-10 years for returns |
| Competition | Intense competition for deals |
What is bad about venture capitalists?
High Pressure for Rapid Growth
Venture capitalists often push startups to grow at an unsustainable pace to achieve quick returns. This pressure can lead to:
See Also I Work for a Vc Company That S Not Looking for Unicorns is There Any Chance They Can Succeed How Does This Even Make Sense
I Work for a Vc Company That S Not Looking for Unicorns is There Any Chance They Can Succeed How Does This Even Make Sense- Burnout among employees due to excessive workloads.
- Compromised product quality as companies rush to meet unrealistic milestones.
- Short-term decision-making that may harm long-term sustainability.
Loss of Control for Founders
When venture capitalists invest, they often demand significant control over the company. This can result in:
- Reduced autonomy for founders in making key decisions.
- Conflicts between investors and founders over the company's direction.
- Potential dilution of the founder's equity and influence over time.
Focus on Profit Over Mission
Venture capitalists prioritize financial returns, which can clash with a startup's original mission. This may lead to:
See Also How Do Investment Banking Venture Capital and Private Equity Differ in Terms of Prestige
How Do Investment Banking Venture Capital and Private Equity Differ in Terms of Prestige- Abandonment of core values to meet investor expectations.
- Ethical compromises in pursuit of profitability.
- Loss of customer trust if the company shifts focus away from its initial purpose.
High Risk of Failure
Startups backed by venture capital often face immense pressure to succeed, but the reality is:
- Most startups fail, leading to significant financial losses for all parties involved.
- Investors may pull funding if milestones are not met, leaving the company stranded.
- Employees may lose jobs if the company cannot sustain operations.
Equity Dilution and Valuation Issues
Venture capital funding often comes at the cost of equity, which can create challenges such as:
- Reduced ownership for founders and early employees.
- Overvaluation of the company, leading to difficulties in future funding rounds.
- Complex cap tables that can complicate decision-making and future investments.
What is the dark side of venture capital?

High Pressure and Burnout
Venture capital often creates an environment of high pressure and burnout for founders and employees. The constant need to meet aggressive growth targets and deliver returns to investors can lead to:
- Excessive working hours that compromise work-life balance.
- Mental health issues such as anxiety and depression due to relentless stress.
- High turnover rates as employees struggle to cope with the demands.
Loss of Control for Founders
One of the significant downsides of venture capital is the potential loss of control for founders. When investors come on board, they often demand:
- Equity stakes that dilute the founder's ownership.
- Decision-making power in key business strategies.
- Pressure to pivot the business model, sometimes against the founder's vision.
Short-Term Focus Over Long-Term Vision
Venture capital investors often prioritize short-term gains over the long-term vision of the company. This can lead to:
- Rushed product launches that may compromise quality.
- Overemphasis on scaling at the expense of sustainable growth.
- Neglect of core values in pursuit of rapid profitability.
Inequality and Exclusivity
The venture capital ecosystem is often criticized for its inequality and exclusivity. Key issues include:
- Limited access for underrepresented founders, such as women and minorities.
- Geographic bias, with most funding concentrated in tech hubs like Silicon Valley.
- Networking barriers that favor those with existing connections in the industry.
Misaligned Incentives
Misaligned incentives between founders and investors can create significant challenges. Common problems include:
- Conflicting goals, where investors prioritize exits while founders focus on building a lasting company.
- Pressure to exit early, potentially undervaluing the company's long-term potential.
- Overvaluation risks that can lead to unsustainable expectations and eventual down rounds.
What is a disadvantage of venture capital?
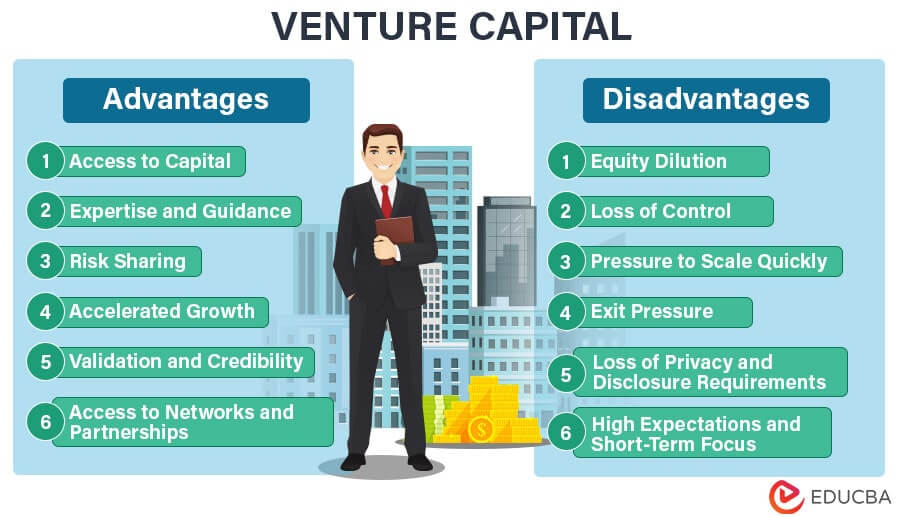
Loss of Control and Ownership
One significant disadvantage of venture capital is the potential loss of control and ownership over your business. When you accept venture capital funding, investors often require equity in exchange, which means they gain a say in how the company is run. This can lead to:
- Dilution of ownership: Founders may own a smaller percentage of their company.
- Decision-making interference: Investors may push for strategies that prioritize short-term gains over long-term vision.
- Pressure to exit: Investors may push for a sale or IPO to realize returns, even if it doesn’t align with the founder’s goals.
High Expectations and Pressure
Venture capitalists expect high returns on their investments, which can create immense pressure on startups. This pressure can manifest in several ways:
- Aggressive growth targets: Startups may be forced to scale prematurely, risking stability.
- Focus on profitability: The need to deliver quick results can overshadow innovation and long-term planning.
- Stress on founders: The constant demand for performance can lead to burnout and strained relationships within the team.
Equity Dilution
Accepting venture capital often means giving up a portion of your company’s equity. This equity dilution can have long-term consequences:
- Reduced financial rewards: Founders may receive a smaller share of profits or proceeds from a sale.
- Limited future funding options: High equity stakes for investors can deter future investors or complicate additional funding rounds.
- Loss of autonomy: With more stakeholders, decision-making becomes more complex and less flexible.
Short-Term Focus
Venture capitalists often prioritize short-term gains over long-term sustainability, which can negatively impact a startup’s trajectory:
- Rushed product development: Quality may suffer as the focus shifts to meeting investor timelines.
- Neglect of core values: The company’s mission and culture may be compromised to meet financial targets.
- Risk of failure: Overemphasis on rapid growth can lead to unsustainable practices and eventual collapse.
Stringent Terms and Conditions
Venture capital agreements often come with stringent terms and conditions that can be restrictive for startups:
- Liquidation preferences: Investors may get paid first in the event of a sale, leaving little for founders.
- Board seats: Investors may demand board representation, influencing key decisions.
- Reporting requirements: Startups may face rigorous reporting and transparency demands, adding administrative burdens.
What percent of VC firms fail?

What Percentage of VC Firms Fail?
The failure rate of venture capital (VC) firms is estimated to be between 40% to 50%. This means that nearly half of all VC firms do not achieve their intended goals or fail to deliver returns to their investors. The high failure rate is attributed to several factors, including market volatility, poor investment decisions, and the inherent risks associated with early-stage startups.
- Market Volatility: Economic downturns and market shifts can drastically impact the performance of startups, leading to losses for VC firms.
- Poor Investment Decisions: Investing in startups with unproven business models or weak management teams increases the likelihood of failure.
- High Competition: The competitive nature of the VC industry makes it challenging for firms to secure the best deals and generate returns.
Why Do VC Firms Fail?
VC firms fail for a variety of reasons, many of which are tied to the high-risk nature of their investments. Startups often operate in uncertain markets, and even promising companies can fail due to unforeseen challenges. Additionally, VC firms must navigate complex regulatory environments and manage relationships with limited partners (LPs), which can further complicate their operations.
- Startup Failures: Many startups fail to achieve product-market fit, leading to losses for their investors.
- Regulatory Challenges: Compliance with evolving regulations can strain resources and impact profitability.
- LP Expectations: Failing to meet the return expectations of limited partners can lead to a loss of trust and funding.
How Do VC Firms Measure Success?
VC firms measure success primarily through return on investment (ROI) and the number of successful exits, such as IPOs or acquisitions. A firm's reputation and ability to attract top-tier startups also play a significant role in determining its success. However, even successful firms face challenges, as the industry is highly cyclical and dependent on market conditions.
- ROI: The primary metric for evaluating a VC firm's performance.
- Exits: Successful exits are critical for generating returns and building a firm's track record.
- Reputation: A strong reputation helps attract high-quality startups and investors.
What Are the Risks for VC Firms?
The risks for VC firms are multifaceted, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. Investing in early-stage startups is inherently risky, as many fail to achieve profitability. Additionally, VC firms must contend with macroeconomic factors, such as interest rate changes and global economic instability, which can impact their portfolios.
- Financial Losses: Startups often require significant capital with no guarantee of success.
- Reputational Damage: Poor investment decisions can harm a firm's reputation and ability to raise future funds.
- Macroeconomic Factors: External economic conditions can negatively affect portfolio performance.
How Can VC Firms Mitigate Failure Risks?
VC firms can mitigate failure risks by adopting diversified investment strategies, conducting thorough due diligence, and building strong relationships with portfolio companies. Additionally, staying informed about market trends and leveraging data-driven decision-making can help firms make more informed investment choices.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across multiple sectors and stages reduces risk.
- Due Diligence: Rigorous evaluation of startups before investing minimizes the likelihood of failure.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leveraging analytics and market insights improves investment outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the most challenging aspect of being a Venture Capitalist?
One of the most challenging aspects of being a Venture Capitalist is the high level of uncertainty involved in investments. Unlike traditional investment avenues, startups are inherently risky, and a significant percentage of them fail. This means that VCs must be prepared to lose their investments in many cases, which can be emotionally and financially taxing. Additionally, the pressure to identify the next big thing before others do adds to the stress and difficulty of the role.
How does the pressure to deliver returns affect Venture Capitalists?
The pressure to deliver returns is immense for Venture Capitalists, as they are often managing funds from limited partners who expect high returns on their investments. This pressure can lead to long hours, constant networking, and the need to stay ahead of market trends. The fear of missing out on a potentially lucrative deal can also lead to rushed decisions, which may not always pan out as expected. This relentless pressure can take a toll on both personal and professional life.
What are the emotional challenges faced by Venture Capitalists?
Venture Capitalists often face significant emotional challenges, particularly when dealing with the failure of portfolio companies. Investing in startups is not just a financial commitment but also an emotional one, as VCs often build close relationships with the founders. Watching a company they believed in fail can be heartbreaking. Moreover, the constant need to balance optimism with realism, and to manage the expectations of both founders and limited partners, can be emotionally draining.
How does the competitive nature of the industry impact Venture Capitalists?
The competitive nature of the venture capital industry is another major challenge. With so many VCs vying for the same deals, it can be difficult to stand out and secure investments in the most promising startups. This competition can lead to higher valuations and more stringent terms, which can reduce potential returns. Additionally, the need to constantly network and build relationships with founders, other investors, and industry experts can be exhausting and time-consuming, leaving little room for personal downtime.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles