Do Vcs Fund Nonprofits if Not How Else Could They Get Funded From Private Investors

Venture capitalists (VCs) traditionally focus on funding high-growth startups with the potential for significant returns, leaving nonprofits in a challenging position when seeking private investment. Unlike for-profit ventures, nonprofits prioritize social impact over financial gains, making them less attractive to VCs. However, this does not mean nonprofits are entirely excluded from private funding. Alternative models, such as impact investing, philanthropic venture capital, and social impact bonds, have emerged to bridge the gap. These approaches allow private investors to support nonprofits while aligning financial returns with measurable social outcomes. Exploring these innovative funding mechanisms can unlock new opportunities for nonprofits to thrive in a competitive financial landscape.
Do VCs Fund Nonprofits? If Not, How Else Could They Get Funded From Private Investors?
1. Do Venture Capitalists (VCs) Typically Fund Nonprofits?
Venture capitalists (VCs) generally do not fund nonprofits because their primary goal is to generate financial returns on their investments. Nonprofits, by nature, are mission-driven organizations that reinvest their profits into their causes rather than distributing them to shareholders. This lack of financial return makes nonprofits less attractive to VCs, who seek high-growth, for-profit ventures. However, some VCs may support nonprofits through philanthropic initiatives or impact investing, but this is not their core focus.
See Also What is an Economic Venture?
What is an Economic Venture?2. What Are Alternative Funding Sources for Nonprofits?
Nonprofits can explore various alternative funding sources to secure financial support. These include grants from foundations, corporate sponsorships, individual donations, and government funding. Additionally, nonprofits can engage in earned-income activities, such as selling products or services, to generate revenue. Another innovative approach is crowdfunding, which leverages online platforms to raise small amounts of money from a large number of people.
3. How Can Nonprofits Attract Private Investors?
To attract private investors, nonprofits must demonstrate their social impact and financial sustainability. They can do this by presenting a clear mission, measurable outcomes, and a solid business plan. Nonprofits can also explore social impact bonds or program-related investments (PRIs), which allow private investors to support social causes while potentially earning a return on their investment. Building strong relationships with high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) and family offices can also be beneficial.
See AlsoDid You Sacrifice Your Career to Raise Your Kids?4. What Role Do Impact Investors Play in Nonprofit Funding?
Impact investors are individuals or organizations that seek to generate both social and financial returns. They are more likely to fund nonprofits compared to traditional VCs because they prioritize social impact alongside profitability. Nonprofits can appeal to impact investors by showcasing their ability to address pressing social issues and deliver measurable results. Impact investing often involves patient capital, which provides nonprofits with the time needed to achieve their goals.
5. Can Nonprofits Partner with For-Profit Entities for Funding?
Yes, nonprofits can form strategic partnerships with for-profit entities to secure funding. These partnerships can take various forms, such as cause-related marketing, joint ventures, or corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. For example, a nonprofit focused on environmental conservation might partner with a sustainable business to raise funds and awareness. Such collaborations can provide nonprofits with financial resources, expertise, and access to new networks.
See Also Why Do Venture Capitalists Replace Founders of Startups?
Why Do Venture Capitalists Replace Founders of Startups?| Funding Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Grants | Funds provided by foundations or government agencies for specific projects or initiatives. |
| Corporate Sponsorships | Financial support from businesses in exchange for brand visibility or alignment with a cause. |
| Individual Donations | Contributions from private individuals, often driven by personal connections to the cause. |
| Earned Income | Revenue generated through the sale of goods or services related to the nonprofit's mission. |
| Crowdfunding | Online campaigns to raise small amounts of money from a large number of people. |
Do venture capitalists fund nonprofits?

What is the Role of Venture Capitalists in Funding Nonprofits?
Venture capitalists typically focus on investing in for-profit businesses with high growth potential. However, their role in funding nonprofits is limited due to the nature of nonprofit organizations, which prioritize social impact over financial returns. While venture capitalists may not directly fund nonprofits, they sometimes support social enterprises or hybrid models that blend profit-making with social missions. These models align more closely with the venture capitalist's goal of achieving financial returns while creating societal impact.
See Also What Do Operations Roles Look Like at a Venture Capital Firm?
What Do Operations Roles Look Like at a Venture Capital Firm?- Venture capitalists primarily invest in for-profit businesses.
- Nonprofits focus on social impact rather than financial returns.
- Some venture capitalists support social enterprises or hybrid models.
Can Nonprofits Attract Venture Capital Funding?
Nonprofits generally do not attract traditional venture capital funding because they lack the profit-driven structure that venture capitalists seek. However, certain nonprofits with innovative models or those operating as social enterprises may attract funding from impact investors or venture philanthropists. These investors are more interested in achieving measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial sustainability.
- Traditional venture capital focuses on profit-driven structures.
- Nonprofits may attract impact investors or venture philanthropists.
- Innovative nonprofit models can align with investor goals.
What Are the Alternatives to Venture Capital for Nonprofits?
Nonprofits often rely on alternative funding sources such as grants, donations, and government funding. Additionally, they may explore social impact bonds, crowdfunding, or partnerships with corporations. These alternatives are better suited to the nonprofit model, as they do not require equity stakes or financial returns, which are central to venture capital investments.
See Also What Motivates You to Work as a Venture Capitalist or an Angel Investor
What Motivates You to Work as a Venture Capitalist or an Angel Investor- Nonprofits rely on grants and donations.
- Government funding is a common source for nonprofits.
- Social impact bonds and crowdfunding are emerging alternatives.
Social enterprises differ from traditional nonprofits in that they operate with a dual focus on generating financial returns and creating social impact. This hybrid model makes them more attractive to venture capitalists and impact investors. Unlike traditional nonprofits, social enterprises often reinvest profits into their mission, creating a sustainable cycle of funding and impact.
- Social enterprises focus on both financial returns and social impact.
- They are more attractive to venture capitalists and impact investors.
- Profits are reinvested to sustain their mission.
What Are the Challenges for Nonprofits Seeking Venture Capital?
Nonprofits face significant challenges when seeking venture capital funding. These include the lack of a profit-driven model, the inability to offer equity stakes, and the misalignment of goals between nonprofits and venture capitalists. Additionally, venture capitalists often require measurable financial returns, which nonprofits cannot guarantee due to their focus on social impact.
- Nonprofits lack a profit-driven model.
- They cannot offer equity stakes to investors.
- Goals of nonprofits and venture capitalists often misalign.
Can nonprofits be privately funded?
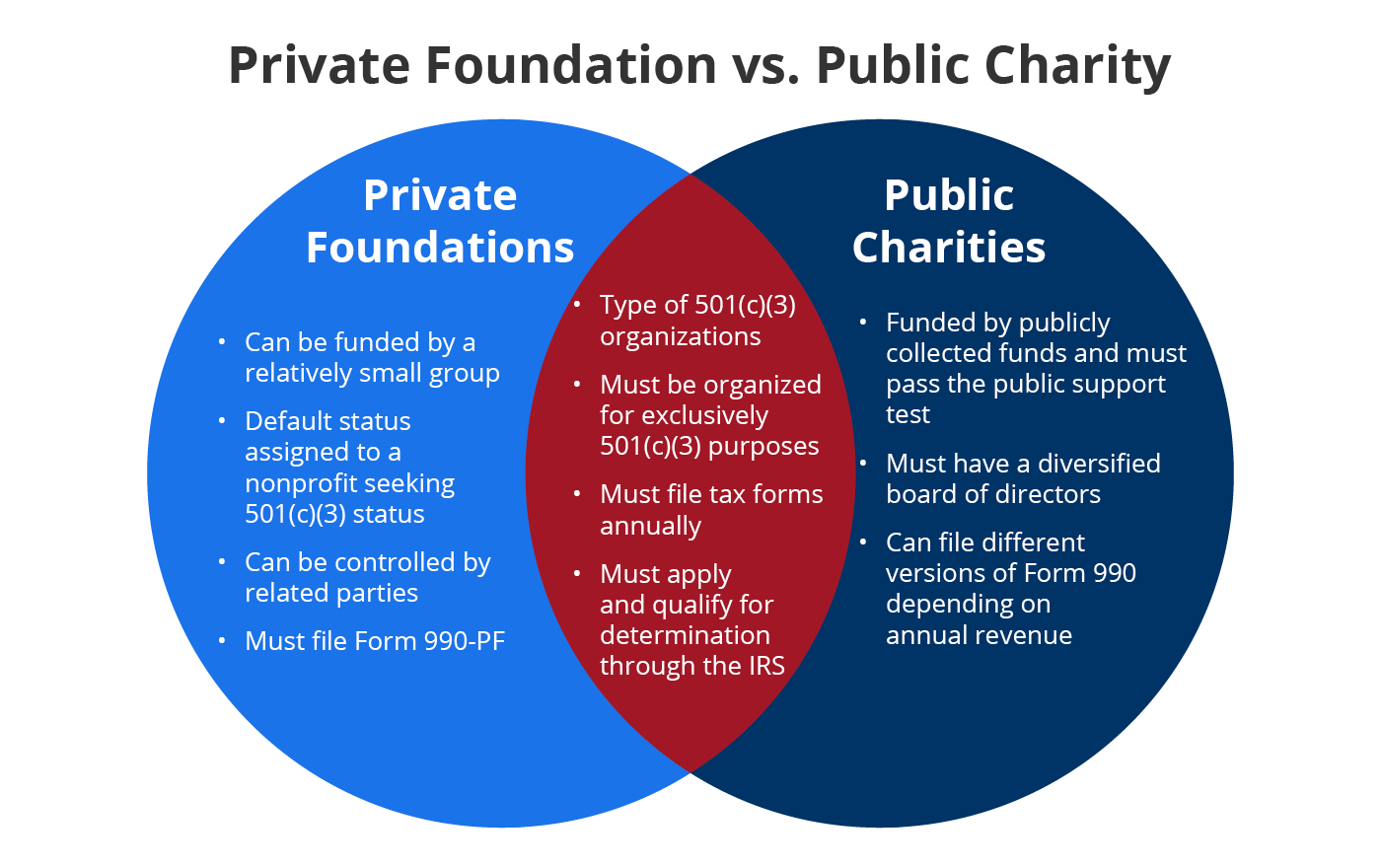
What Does Privately Funded Mean for Nonprofits?
Privately funded nonprofits receive their financial support from private sources rather than government grants or public donations. These sources can include:
- Individual donors who contribute personal funds.
- Private foundations established by individuals, families, or corporations.
- Corporate sponsorships where businesses provide funding in exchange for recognition or alignment with their values.
How Do Nonprofits Benefit from Private Funding?
Private funding offers nonprofits several advantages, including:
- Flexibility in how funds are used, as private donors often impose fewer restrictions than government grants.
- Stability through long-term partnerships with private entities.
- Innovation by enabling nonprofits to pilot new programs without bureaucratic hurdles.
Are There Legal Restrictions on Private Funding for Nonprofits?
While private funding is allowed, nonprofits must adhere to specific legal guidelines, such as:
- Ensuring that funds are used for charitable purposes as defined by law.
- Avoiding private benefit to individuals, which could jeopardize their tax-exempt status.
- Complying with reporting requirements to maintain transparency and accountability.
What Are the Challenges of Relying on Private Funding?
Privately funded nonprofits may face certain challenges, including:
- Dependency on a limited number of donors, which can be risky if funding decreases.
- Donor influence where private funders may attempt to steer the organization's mission or activities.
- Fundraising pressure to continuously secure private donations to sustain operations.
How Can Nonprofits Attract Private Funding?
To successfully attract private funding, nonprofits can:
- Develop a compelling mission statement that resonates with potential donors.
- Build strong relationships with private individuals, foundations, and corporations.
- Demonstrate impact and accountability through transparent reporting and success stories.
How do non profit organizations get funding?
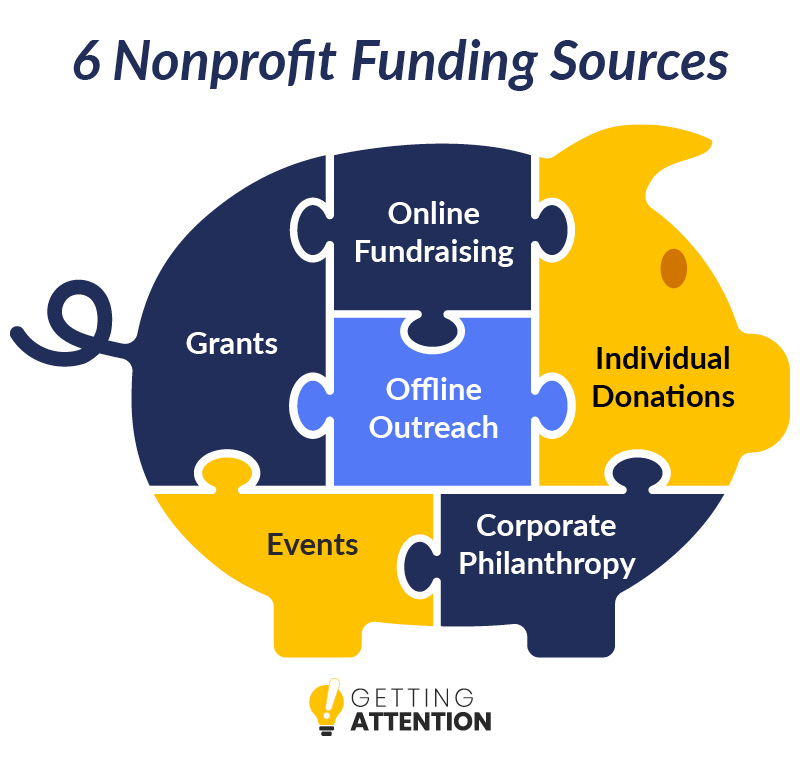
1. Grants from Foundations and Governments
Non-profit organizations often secure funding through grants provided by foundations, government agencies, and other institutions. These grants are typically awarded based on specific criteria, such as the organization's mission, project proposals, and alignment with the funder's goals. To access these funds, non-profits must submit detailed applications, including budgets, objectives, and expected outcomes. Some well-known grant providers include the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and government programs like the National Endowment for the Arts.
- Research potential grant opportunities that align with your mission.
- Prepare a compelling grant proposal with clear objectives and measurable outcomes.
- Ensure compliance with all application requirements and deadlines.
2. Individual Donations
Individual donations are a significant source of funding for non-profits. These contributions can come from one-time gifts, monthly donations, or major gifts from high-net-worth individuals. Non-profits often use fundraising campaigns, events, and online platforms to attract individual donors. Building strong relationships with donors through personalized communication and transparency is key to sustaining this funding stream.
- Create engaging fundraising campaigns to inspire donations.
- Leverage social media and email marketing to reach a wider audience.
- Offer donor recognition programs to show appreciation and encourage repeat contributions.
3. Corporate Sponsorships and Partnerships
Many non-profits collaborate with businesses through corporate sponsorships and partnerships. Companies often support non-profits as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. In return, non-profits may offer visibility through branding opportunities, event sponsorships, or co-branded campaigns. These partnerships can provide both financial support and in-kind contributions, such as products or services.
- Identify companies with values that align with your mission.
- Develop a sponsorship proposal highlighting mutual benefits.
- Maintain strong relationships with corporate partners through regular updates and acknowledgments.
4. Fundraising Events
Fundraising events are a popular way for non-profits to raise money while engaging their community. These events can range from galas and auctions to marathons and virtual fundraisers. Successful events require careful planning, effective promotion, and strong volunteer support. They not only generate funds but also increase awareness and strengthen donor relationships.
- Choose an event format that resonates with your target audience.
- Secure sponsors and partners to offset costs and maximize revenue.
- Use social media and local media to promote the event effectively.
5. Membership Fees and Service Revenue
Some non-profits generate income through membership fees or by offering services. For example, museums, professional associations, and educational institutions often charge membership fees to access exclusive benefits. Additionally, non-profits may offer workshops, training programs, or consulting services to generate revenue. This approach allows organizations to diversify their funding sources while fulfilling their mission.
- Develop a membership program with attractive benefits to encourage sign-ups.
- Offer high-quality services that align with your organization's expertise.
- Use revenue generated to reinvest in programs and expand your impact.
How do VCs get funding?

1. Raising Capital from Limited Partners (LPs)
Venture Capital (VC) firms primarily get funding by raising capital from Limited Partners (LPs). These LPs are typically institutional investors, such as pension funds, endowments, insurance companies, and high-net-worth individuals. The process involves:
- Pitching the Fund: VC firms present their investment thesis, track record, and strategy to potential LPs to attract commitments.
- Negotiating Terms: Once LPs show interest, terms such as management fees, carried interest, and fund duration are negotiated.
- Closing the Fund: After securing commitments, the VC firm closes the fund and begins deploying capital into startups.
2. Management Fees and Carried Interest
VC firms generate revenue through management fees and carried interest. These are structured as follows:
- Management Fees: Typically 2% of the total fund size, charged annually to cover operational costs.
- Carried Interest: Usually 20% of the profits earned from successful investments, incentivizing VCs to maximize returns.
- Fee Structures: These terms are outlined in the Limited Partnership Agreement (LPA) signed with LPs.
3. Recycling Capital from Exits
VCs often recycle capital from successful exits to fund new investments. This process involves:
- Exiting Investments: Selling portfolio companies through IPOs or acquisitions to generate returns.
- Reinvesting Proceeds: Using a portion of the profits to make follow-on investments in other startups.
- Extending Fund Life: Recycling allows VCs to extend the life of a fund without raising additional capital.
4. Co-Investment Opportunities
VCs sometimes secure additional funding through co-investment opportunities. This involves:
- Partnering with LPs: Allowing LPs to invest directly in specific deals alongside the VC fund.
- Reducing Risk: Sharing the investment risk with co-investors while maintaining control over the deal.
- Enhancing Returns: Leveraging co-investments to amplify returns for both the VC firm and LPs.
5. Fundraising from Corporate Investors
Some VC firms raise funding from corporate investors, such as large corporations seeking strategic investments. The process includes:
- Strategic Alignment: Aligning the VC fund's focus with the corporate investor's business goals.
- Access to Resources: Gaining access to the corporate investor's network, expertise, and resources.
- Joint Ventures: Collaborating on joint ventures or innovation initiatives to drive mutual growth.
Frequently Asked Questions by our Community
Do venture capital firms (VCs) fund nonprofits?
Venture capital firms typically do not fund nonprofits because their primary goal is to generate financial returns for their investors. VCs invest in for-profit startups and businesses with high growth potential, expecting equity or ownership stakes in return. Nonprofits, by definition, are mission-driven organizations that reinvest their profits into their cause rather than distributing them to shareholders. This structure makes them incompatible with the traditional VC funding model.
How can nonprofits attract funding from private investors?
Nonprofits can attract funding from private investors by focusing on innovative funding models such as impact investing or social impact bonds. These models allow investors to support social or environmental causes while potentially earning a return on their investment. Additionally, nonprofits can build strong relationships with philanthropists, family offices, or corporate social responsibility (CSR) programs that align with their mission. Demonstrating measurable impact and transparency is key to gaining investor trust.
What are alternative funding sources for nonprofits besides venture capital?
Nonprofits can explore various alternative funding sources, such as grants from foundations or government agencies, crowdfunding campaigns, and corporate sponsorships. They can also generate revenue through earned income strategies, such as selling products or services related to their mission. Another option is forming partnerships with for-profit entities through cause-related marketing or joint ventures, which can provide financial support while raising awareness for their cause.
Can nonprofits collaborate with venture capital firms in any way?
While VCs typically do not fund nonprofits directly, they can collaborate in other ways. For example, VCs may support social enterprises or hybrid models that combine profit-making with social impact. Nonprofits can also partner with VCs to access their networks, expertise, or resources for scaling their operations. Additionally, some VCs have philanthropic arms or foundations that provide grants or donations to nonprofits aligned with their values.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles