How Do Vc Firms Raise Their Funds?
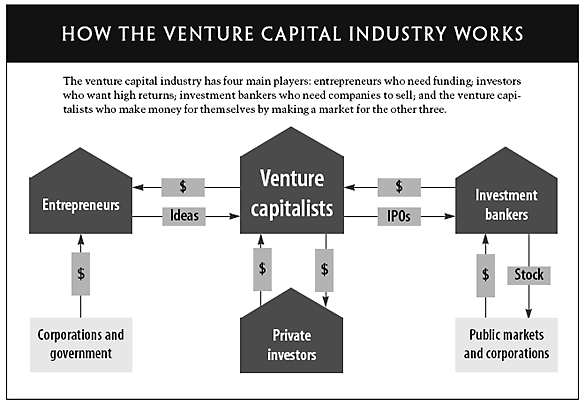
Venture capital (VC) firms play a pivotal role in fueling innovation by investing in high-potential startups and emerging businesses. However, before these firms can allocate funds to promising ventures, they must first raise capital themselves. The process of raising funds for VC firms involves attracting limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, pension funds, and high-net-worth individuals, who commit capital to the firm’s investment funds. This article explores the strategies and mechanisms VC firms use to secure funding, the challenges they face in convincing investors, and the critical role of track records and market conditions in shaping their fundraising success.
How Do VC Firms Raise Their Funds?
Venture capital (VC) firms play a crucial role in funding startups and innovative businesses. However, before they can invest in these companies, they need to raise their own funds. This process involves attracting limited partners (LPs), such as institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and family offices, who provide the capital that VC firms then invest. Below, we explore the key aspects of how VC firms raise their funds.
See Also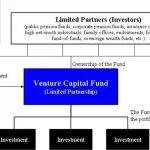 How Do the Different Types of Partners in a Venture Capital Firm Differ General Partner Operating Partner Investment Partner Etc
How Do the Different Types of Partners in a Venture Capital Firm Differ General Partner Operating Partner Investment Partner Etc1. Understanding the Role of Limited Partners (LPs)
Limited partners are the primary source of capital for VC firms. These entities or individuals invest in the VC fund but do not participate in the day-to-day management. LPs include pension funds, endowments, insurance companies, and wealthy individuals. They commit capital to the fund with the expectation of earning significant returns over time. The relationship between VC firms and LPs is governed by a limited partnership agreement, which outlines the terms, fees, and profit-sharing arrangements.
2. The Fundraising Process for VC Firms
The fundraising process for VC firms typically begins with the creation of a pitch deck and an investment thesis. The firm’s partners approach potential LPs, presenting their track record, strategy, and market opportunities. Once LPs express interest, they negotiate terms and sign a commitment letter. The VC firm then closes the fund once it reaches its target size, which can range from $50 million to over $1 billion, depending on the firm’s reputation and focus.
See Also How Do Venture Capital Firms Work?
How Do Venture Capital Firms Work?3. Key Components of a VC Fund Structure
VC funds are structured as limited partnerships, with the VC firm acting as the general partner (GP). The GP manages the fund and makes investment decisions, while LPs provide the capital. The fund’s lifespan is usually 10 years, divided into an investment period (3-5 years) and a harvesting period (5-7 years). During the investment period, the VC firm identifies and invests in startups, while the harvesting period focuses on exiting investments and returning profits to LPs.
4. Fees and Profit Sharing in VC Funds
VC firms charge LPs two main types of fees: a management fee and a carried interest. The management fee, typically 2% of the committed capital, covers operational costs. Carried interest, usually 20% of the profits, is the GP’s share of the returns after LPs receive their initial investment back. This profit-sharing model aligns the interests of the GP and LPs, as both parties benefit from successful investments.
See Also What Are Typical Finders Fees Vcs Are Ready to Pay for a Unique Lead on a Start Up
What Are Typical Finders Fees Vcs Are Ready to Pay for a Unique Lead on a Start Up5. Challenges in Raising Funds for VC Firms
Raising funds is not without challenges. VC firms must demonstrate a strong track record, a clear investment strategy, and the ability to generate high returns. Additionally, competition for LP capital is intense, especially in crowded markets. Economic downturns or poor performance can also make fundraising more difficult. To succeed, VC firms must build trust and credibility with LPs while showcasing their ability to identify and nurture high-potential startups.
| Key Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Limited Partners (LPs) | Investors who provide capital to VC funds but do not manage them. |
| General Partner (GP) | The VC firm that manages the fund and makes investment decisions. |
| Management Fee | A fee charged by the GP, typically 2% of the committed capital. |
| Carried Interest | The GP’s share of the profits, usually 20% after LPs recover their investment. |
| Investment Period | The initial 3-5 years of a fund’s lifespan, focused on making investments. |
| Harvesting Period | The final 5-7 years of a fund’s lifespan, focused on exiting investments. |
How does a VC firm raise money?

Understanding the Basics of VC Fundraising
Venture capital (VC) firms raise money by pooling funds from various investors to create a fund. This fund is then used to invest in startups and high-growth companies. The process involves several key steps:
- Identify Limited Partners (LPs): These are institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, or entities that contribute capital to the VC fund.
- Set Fund Objectives: Define the investment strategy, target industries, and expected returns to attract LPs.
- Legal Structuring: Establish the fund as a legal entity, often a limited partnership, to manage investments and liabilities.
Key Players in VC Fundraising
Several stakeholders play crucial roles in the fundraising process for a VC firm:
- General Partners (GPs): The managing team responsible for making investment decisions and managing the fund.
- Limited Partners (LPs): Investors who provide capital but do not participate in day-to-day management.
- Fund Administrators: Professionals who handle accounting, compliance, and reporting for the fund.
Stages of VC Fundraising
Raising a VC fund typically follows a structured process:
- Fund Formation: Legal and operational setup of the fund, including drafting the Limited Partnership Agreement (LPA).
- Marketing the Fund: Presenting the fund's strategy and track record to potential LPs through roadshows and meetings.
- Closing the Fund: Finalizing commitments from LPs and reaching the target fund size.
Challenges in VC Fundraising
VC firms often face hurdles during the fundraising process:
- Competition: Standing out among numerous VC firms vying for the same LPs.
- Economic Conditions: Market downturns can make LPs hesitant to commit capital.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating complex legal and regulatory requirements.
Strategies for Successful VC Fundraising
To ensure a successful fundraising round, VC firms employ specific strategies:
- Build a Strong Track Record: Demonstrating past successes attracts LPs.
- Leverage Networks: Utilizing existing relationships to connect with potential investors.
- Transparency: Providing clear and detailed information about the fund's strategy and risks.
How do you raise venture capital funds?

Understanding Venture Capital Funding
Raising venture capital funds involves securing investment from venture capital firms or individual investors who provide capital to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. This process requires a clear understanding of how venture capital works and what investors are looking for.
- Identify your business stage: Venture capitalists typically invest in businesses that have moved beyond the initial startup phase and show potential for rapid growth.
- Research venture capital firms: Look for firms that specialize in your industry or have a history of investing in similar businesses.
- Prepare a compelling pitch: Develop a detailed business plan and presentation that highlights your business model, market opportunity, and growth strategy.
Preparing Your Business for Investment
Before approaching venture capitalists, it's crucial to ensure your business is investment-ready. This involves having a solid foundation and clear growth trajectory.
- Develop a scalable business model: Investors want to see that your business can grow significantly with additional funding.
- Build a strong team: A capable and experienced team increases your chances of securing investment.
- Create a detailed financial plan: Include projections, revenue models, and a clear use of funds to demonstrate how the investment will be utilized.
Crafting a Winning Pitch Deck
A pitch deck is a critical tool for communicating your business vision and potential to venture capitalists. It should be concise, visually appealing, and compelling.
- Start with a strong introduction: Clearly explain your business, mission, and value proposition in the first few slides.
- Highlight market opportunity: Use data and research to show the size and potential of your target market.
- Showcase traction and milestones: Provide evidence of your business's progress, such as customer acquisition, revenue growth, or product development.
Networking and Building Relationships
Building relationships with venture capitalists and other investors is essential for raising funds. Networking can open doors to potential investors and provide valuable insights.
- Attend industry events: Participate in conferences, pitch competitions, and networking events to meet potential investors.
- Leverage your network: Use existing connections to get introductions to venture capitalists or angel investors.
- Engage with investors online: Utilize platforms like LinkedIn to connect with investors and share updates about your business.
Negotiating Terms and Closing the Deal
Once you've attracted interest from venture capitalists, the next step is negotiating the terms of the investment and finalizing the deal.
- Understand term sheets: Familiarize yourself with the key components of a term sheet, such as valuation, equity, and investor rights.
- Seek legal advice: Work with a lawyer who specializes in venture capital to ensure the terms are fair and favorable.
- Finalize due diligence: Be prepared to provide detailed information about your business, including financials, legal documents, and operational details.
How to get funding from venture capital firms?

Understanding Venture Capital Firms
Venture capital firms are investment companies that provide funding to startups and small businesses with high growth potential. To secure funding, it is essential to understand their investment criteria and processes. Here are key points to consider:
- Research the firm's portfolio to ensure alignment with your industry and business model.
- Understand their investment stages (seed, early-stage, or growth-stage) to target the right firms.
- Identify the decision-makers within the firm, such as partners or associates, to tailor your pitch.
Preparing a Compelling Pitch Deck
A pitch deck is a critical tool to capture the interest of venture capital firms. It should clearly communicate your business idea, market potential, and growth strategy. Key elements to include are:
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the problem your product or service solves.
- Solution: Showcase your unique value proposition and how it addresses the problem.
- Market Opportunity: Provide data on the size and growth potential of your target market.
Building a Strong Network
Networking plays a crucial role in gaining access to venture capital firms. Building relationships with investors and industry professionals can increase your chances of securing funding. Steps to take include:
- Attend industry events and conferences to meet potential investors.
- Leverage warm introductions through mutual connections to get noticed.
- Engage with mentors or advisors who have experience in fundraising.
Demonstrating Traction and Metrics
Venture capital firms look for evidence of traction and growth potential before investing. To impress investors, focus on:
- Revenue Growth: Show consistent and scalable revenue streams.
- Customer Acquisition: Highlight your ability to attract and retain customers.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Present metrics like customer lifetime value (CLV) and churn rate.
Negotiating Terms and Closing the Deal
Once a venture capital firm shows interest, it is crucial to negotiate favorable terms and finalize the deal. Key considerations include:
- Valuation: Agree on a fair valuation for your company based on market standards.
- Equity Stake: Determine the percentage of equity you are willing to offer in exchange for funding.
- Legal Agreements: Work with legal experts to review and finalize term sheets and contracts.
How to raise venture capital funding for your business?

Understanding Venture Capital and Its Requirements
Venture capital (VC) is a form of private equity financing that investors provide to early-stage, high-potential startups. To raise venture capital, you must first understand what VCs look for in a business. Typically, they seek:
- Scalability: A business model that can grow rapidly and generate significant returns.
- Innovation: A unique product or service that solves a pressing problem or disrupts an industry.
- Strong Team: A capable and experienced team with a proven track record.
- Market Potential: A large and growing target market.
- Traction: Evidence of customer interest, such as sales, partnerships, or user growth.
Preparing a Compelling Pitch Deck
A pitch deck is a critical tool for attracting venture capital. It should clearly communicate your business idea, market opportunity, and growth strategy. Key elements to include are:
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the problem your business solves.
- Solution: Explain how your product or service addresses the problem.
- Market Size: Provide data on the total addressable market (TAM) and growth potential.
- Business Model: Outline how your company will generate revenue.
- Financial Projections: Present realistic and data-driven financial forecasts.
Identifying the Right Venture Capital Firms
Not all venture capital firms are the same. To increase your chances of success, target firms that align with your industry, stage of development, and funding needs. Steps to identify the right VCs include:
- Research: Look for firms that have invested in similar businesses or industries.
- Network: Leverage your professional network to get warm introductions.
- Stage Fit: Ensure the firm invests in businesses at your growth stage (seed, Series A, etc.).
- Portfolio Alignment: Review the firm’s portfolio to see if your business complements their existing investments.
- Reputation: Consider the firm’s reputation, track record, and value-add beyond funding.
Building Relationships with Investors
Raising venture capital is not just about pitching; it’s about building long-term relationships. To establish trust and credibility with investors:
- Engage Early: Start building relationships before you need funding.
- Be Transparent: Share both successes and challenges openly.
- Show Progress: Demonstrate consistent growth and milestones achieved.
- Seek Feedback: Use investor feedback to refine your business strategy.
- Follow Up: Maintain regular communication to keep investors updated.
Negotiating Terms and Closing the Deal
Once a VC shows interest, the negotiation phase begins. This involves agreeing on terms that benefit both parties. Key considerations include:
- Valuation: Determine a fair valuation for your company.
- Equity Stake: Decide how much equity you are willing to give up.
- Control: Clarify decision-making rights and board representation.
- Milestones: Set clear milestones tied to future funding rounds.
- Legal Documentation: Work with legal experts to draft and review term sheets and agreements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the primary sources of funding for venture capital firms?
Venture capital firms primarily raise their funds from institutional investors, such as pension funds, endowments, and insurance companies. These entities provide large sums of capital due to their ability to invest in high-risk, high-reward opportunities. Additionally, high-net-worth individuals and family offices often contribute to venture capital funds, seeking diversification and potential high returns. Some VC firms also receive funding from corporations looking to invest in innovative startups that align with their strategic interests.
How do venture capital firms structure their funds?
Venture capital firms typically structure their funds as limited partnerships, where the firm acts as the general partner (GP) and the investors are limited partners (LPs). The GP manages the fund and makes investment decisions, while the LPs provide the capital and have limited liability. The fund operates for a fixed term, usually 10 years, during which the VC firm invests in startups and works to generate returns. At the end of the term, the fund is liquidated, and profits are distributed to the LPs after deducting management fees and carried interest.
What is the role of management fees and carried interest in VC fundraising?
Management fees and carried interest are critical components of how venture capital firms raise and manage their funds. Management fees, typically around 2% of the committed capital, cover the operational costs of the VC firm, such as salaries and office expenses. Carried interest, usually 20% of the profits, serves as the primary incentive for the VC firm to generate high returns. This structure aligns the interests of the VC firm and its investors, as the firm only earns significant profits if the fund performs well.
Can venture capital firms raise funds from public markets?
While most venture capital firms rely on private funding sources, some have explored raising capital from public markets. For example, certain VC firms have gone public or created special-purpose acquisition companies (SPACs) to access broader investor bases. However, this approach is less common due to the regulatory complexities and the preference for private funding structures that offer more flexibility and confidentiality. Public market fundraising is more typical for later-stage investment firms or those with a diversified portfolio of assets.
Leave a Reply

Our Recommended Articles